When it comes to hydraulic and pneumatic systems, understanding different thread types is critical to ensuring proper fitting and sealing.
One of the most commonly used thread types is the British Standard Pipe Taper (BSPT) thread. In this article, we will explore what BSPT threads are, their characteristics, applications, and how they compare to other thread types.
If you have any questions about BSPT threads, feel free to contact us at any time.
What is BSPT Thread?

BSPT stands for British Standard Pipe Taper Thread. It is a type of thread commonly used in piping and fitting applications to ensure a tight, leak-proof seal. BSPT threads are tapered, meaning their diameter decreases towards the end of the thread, creating a secure fit when tightened.
Below is a table showing common BSPT thread sizes and dimensions:
| BSPT Thread Size | Outer Diameter (mm) | TPI (Threads Per Inch) |
|---|---|---|
| 1/8″ | 9.728 | 28 |
| 1/4″ | 13.157 | 19 |
| 3/8″ | 16.662 | 19 |
| 1/2″ | 20.955 | 14 |
| 3/4″ | 26.441 | 14 |
| 1″ | 33.249 | 11 |
Key Characteristics of BSPT Thread
- Tapered Profile: The most distinctive feature of a BSPT thread is its tapered profile. This taper ensures a tight seal as the threads are screwed together, making it ideal for applications where leakage cannot be tolerated.
- 55-degree Included Angle: The angle between the flanks of the thread is 55 degrees. This angle is a standard for many types of pipe threads.
- 1:16 Taper: The taper of the thread is 1:16, meaning that for every 16 units of length along the thread, the diameter increases by 1 unit.
- British Standard: BSPT is a British standard, and its dimensions and tolerances are specified in British Standards documents.
Why Use BSPT Thread?
BSPT threads are widely used in various industries, including:
- Hydraulic Systems: Due to their ability to form a tight seal, BSPT threads are commonly used in hydraulic systems for connecting components like valves, fittings, and hoses.
- Pneumatic Systems: BSPT threads are also used in pneumatic systems for similar reasons.
- General Engineering: BSPT threads find applications in a wide range of general engineering applications where a reliable seal is required.
BSPT Thread Standards
BSPT threads are governed by various international standards to ensure compatibility and consistency. The most common standards include:
- ISO 7-1: International standard for pipe threads where pressure-tight joints are made.
- BS 21: British standard for pipe threads.
- JIS B0203: Japanese industrial standard for pipe threads.
While the core specifications remain consistent, slight differences in measurement methods or tolerances may exist between countries. These are typically addressed through coordination and adherence to ISO standards.
BSPT vs. Other Threads
BSPT vs. NPT
- Taper Angle: The taper angle of BSPT is 1 in 16, while the NPT thread has a taper angle of 1 in 16 for the external thread and 1 in 20 for the internal thread. This difference in taper can affect the way the fittings are tightened and the resulting seal.
- Thread Profile: BSPT has an ISO metric 60-degree thread form, while NPT has an American National 60-degree thread form. Although the angles are the same, there are differences in the root and crest shapes, which can impact the compatibility and performance of the threads.
BSPT vs. BSPP
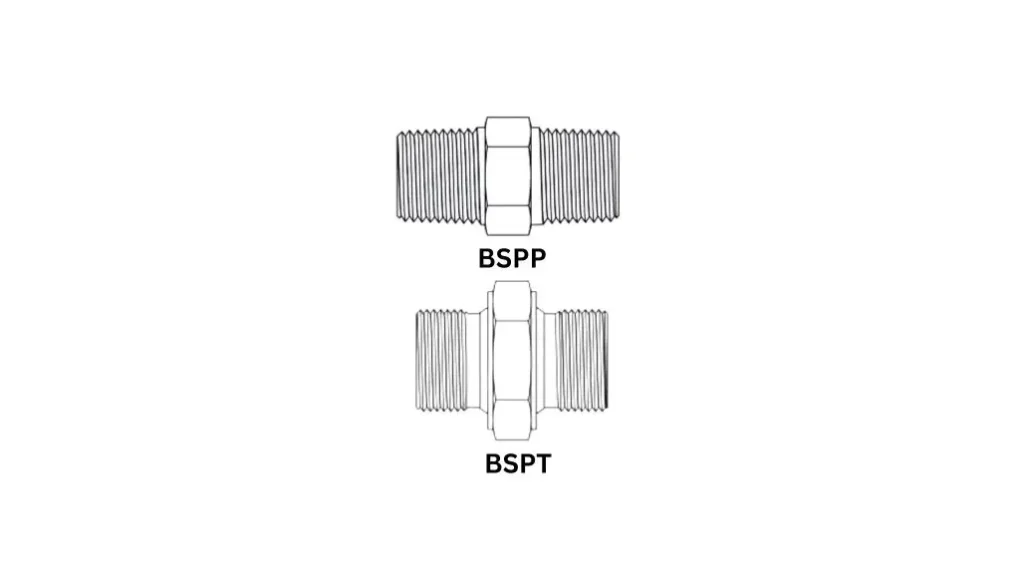
- Taper vs. Parallel: G threads are parallel threads, also known as British Standard Pipe Parallel (BSPP) threads. In contrast, BSPT threads are tapered. G threads require additional sealing methods like sealing washers or thread sealants to create a leak-tight joint, while BSPT’s tapered design often allows for a seal without such additives.
- Application Scenarios: G threads are more commonly used in low-pressure applications where a simple connection is required, while BSPT is preferred for higher-pressure applications.
BSPT vs. G Threads
- Taper vs. Parallel: G threads are parallel threads, also known as British Standard Pipe Parallel (BSPP) threads. In contrast, BSPT threads are tapered. G threads require additional sealing methods like sealing washers or thread sealants to create a leak – tight joint, while BSPT’s tapered design often allows for a seal without such additives.
- Application Scenarios: G threads are more commonly used in low-pressure applications where a simple connection is required, while BSPT is preferred for higher-pressure applications.
How to Select BSPT Threads?
Step 1: Determine Application Requirements
Understand the pressure and sealing needs of your system.
Step 2: Identify Thread Size
Use thread gauges or consult sizing charts to determine the correct thread size.
Step 3: Confirm Standards Compliance
Ensure the thread matches the applicable international or regional standards.
How to Install BSPT Threads?
Step 1: Prepare the Fittings
Inspect the BSPT-threaded fittings for any damage, such as burrs or deformed threads. Clean the threads thoroughly to remove any dirt, debris, or oil.
Step 2: Apply Sealant (Optional)
Although BSPT threads can create a seal without additional sealant in many cases, for extra security or in some specific applications, a suitable thread sealant can be applied. Apply the sealant evenly around the male threads, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Step 3: Start the Assembly
Align the male and female BSPT threads carefully. Start screwing the male fitting into the female fitting by hand. Make sure to turn it in a clockwise direction.
Step 4: Tighten the Fittings
Once the threads are engaged by hand, use a suitable wrench to tighten the fittings further. Do not over-tighten, as this can damage the threads. Use a torque wrench if precise torque values are specified for the application.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding “what is bspt thread” is essential for those working in industries related to piping and fluid systems. BSPT threads, with their unique features, standards, and applications, offer a reliable solution for creating leak-tight connections.
Whether you are in the hydraulic, pneumatic, or plumbing industry, choosing the right thread type and installing it correctly is crucial. If you are interested in our products, you can visit our homepage or ask us for a product catalog.
FAQs About BSPT Thread
How do I know if I have NPT or BSPT?
You can measure the taper angle. If the taper angle is 1 in 16 (approx. 3.6°), it may be BSPT. NPT has a slightly different taper for internal and external threads. Also, you can check the thread profile.
BSPT has an ISO metric 60-degree thread form, while NPT has an American National 60-degree thread form. Another way is to check the markings on the fittings, if available.
Can you tap BSPT to NPT?
Tapping BSPT to NPT is not a straightforward process. Due to the differences in thread profile and taper, it is not recommended to directly tap one thread type into the other.
Specialized tools and procedures would be required, and even then, the resulting connection may not be reliable. It is better to use adapter fittings to connect BSPT and NPT components.
What is the taper angle of BSPT thread?
The taper angle of BSPT thread is 1 in 16, which is approximately 3.6°. This taper angle is crucial for the self-sealing ability of BSPT threads when the fittings are tightened.
How to measure BSPT thread?
To measure BSPT thread, you can use a thread gauge to check the thread pitch (threads per inch). For the diameter, use a caliper to measure the major and minor diameters of the thread. Make sure to measure at multiple points along the thread to ensure accuracy.
What is BSPT thread size?
BSPT thread sizes are designated by a nominal size, such as 1/8, 1/4, 1/2, etc. Each size has specific dimensions for the major diameter, minor diameter, and the number of threads per inch.
For example, a 1/4 BSPT thread has an external thread major diameter of 13.157 mm, an external thread minor diameter of 11.445 mm, and 19 threads per inch.
Where to buy fittings?
You can customize fittings with us. Our brand is Dingfeng, and we have a full range of products. Feel free to contact us at any time.



