Flare fittings are essential components in various fluid systems, offering reliable and leak-free connections. However, not all flare fittings are created equal. Understanding the different types of flare fittings available is crucial for selecting the right components for your specific application. This guide will delve into the key types of flare fittings, including their unique characteristics, applications, and considerations.
We will explore popular options such as AN (Army-Navy), JIC (Joint Industry Conference), 45-degree flare, inverted flare, and more, providing you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and ensure optimal performance in your fluid systems.
What Are Flare Fittings

Flare fittings are a type of mechanical connector used to join metal tubing in various applications, such as automotive, hydraulic, and refrigeration systems.
They are characterized by a unique sealing mechanism: the end of the tubing is “flared,” or expanded and deformed, into a conical shape. This flared end is then inserted into a matching tapered fitting and secured with a nut, creating a tight and leak-proof seal.
Flare fittings offer several advantages, including their ability to withstand high pressures and vibrations, making them suitable for demanding applications. They are also relatively easy to assemble and disassemble, which is beneficial for maintenance and repairs. However, it’s crucial to properly flare the tubing and ensure correct installation to achieve a reliable and leak-free connection.
Types of Flare Fittings

1. Double Flare Fittings
Double flare fittings feature a thicker and more robust flare profile on the tubing. The tubing’s wall is folded over on itself before being flared, creating a stronger and more durable seal. This extra step in the flaring process enhances the fitting’s resistance to fatigue and makes it suitable for applications with higher vibration or fluctuating pressures. Double flare fittings are commonly found in high-performance automotive applications, such as racing vehicles, where reliability and durability are paramount.
2. 45-Degree Flare Fittings
As the name suggests, 45-degree flare fittings utilize a 45-degree angle on the flared end of the tubing. They are a common type found in various applications, including automotive, refrigeration, and general industrial use. 45-degree flare fittings are typically used for lower pressure applications compared to 37-degree flares. They are generally more economical than 37-degree fittings and are easier to assemble and disassemble.
3. 37-Degree Flare Fittings (AN and JIC)
37-degree flare fittings are widely used in high-performance applications such as aerospace, racing, and heavy-duty machinery. They are known for their ability to withstand high pressures and extreme temperatures.
- AN (Army-Navy) fittings are manufactured to strict military specifications, ensuring high quality and reliability. They are commonly found in aerospace applications.
- JIC (Joint Industry Conference) fittings are manufactured to less stringent industrial standards, making them more cost-effective. They are widely used in various industrial and automotive applications.
4. Inverted Flare Fittings
Inverted flare fittings feature a unique design where the flare is located on the inside of the fitting itself, rather than on the end of the tubing. This creates a stronger and more vibration-resistant seal compared to traditional flare fittings. Inverted flare fittings are commonly used in automotive applications, particularly in brake lines and fuel systems, where vibration resistance is crucial.
5. Metric Flare Fittings
Metric flare fittings are designed to metric standards, making them commonly used in European applications. They utilize metric thread sizes and may have different flare angles compared to their imperial counterparts.
| Fitting Type | Flare Angle | Applications | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Double Flare | Varies | High-performance applications, racing | Increased strength and fatigue resistance |
| 45-Degree Flare | 45 degrees | General industrial, automotive (lower pressure) | Easier to assemble, more economical |
| 37-Degree Flare (AN/JIC) | 37 degrees | Aerospace, racing, high-pressure applications | High pressure capability, high quality (AN), more cost-effective (JIC) |
| Inverted Flare | Varies | Automotive (brake lines, fuel systems) | Vibration resistance, strong seal |
| Metric Flare | Varies (metric standards) | European applications | Metric dimensions, may have different flare angles |
Flared Fittings vs Flareless Fittings
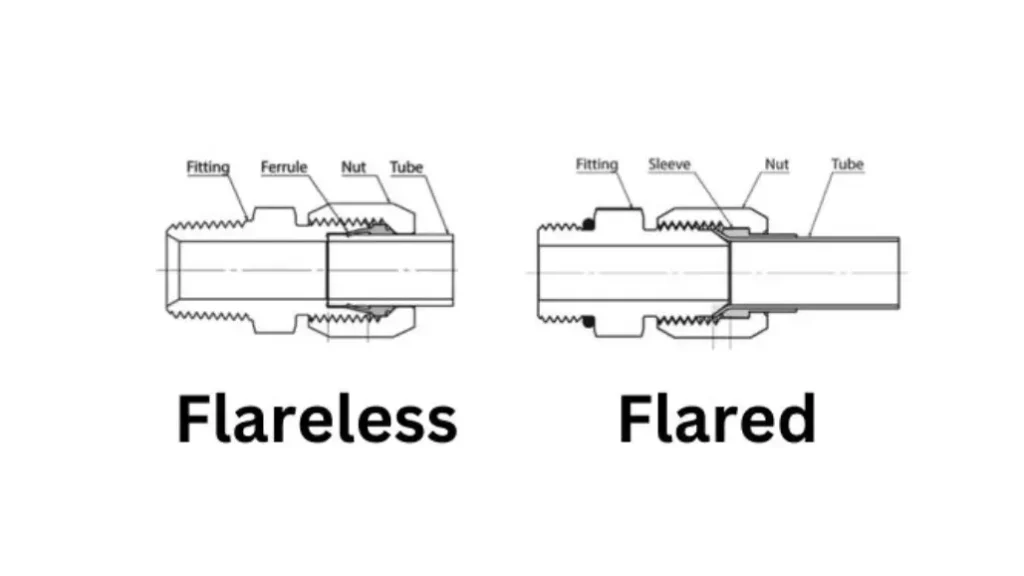
Flared and flareless fittings are both used to connect tubes in fluid systems, but they differ significantly in their design and installation:
Flared Fittings:
- Sealing Mechanism: Create a seal by flaring the end of the tubing at a specific angle (e.g., 37 degrees for AN/JIC) and inserting it into a mating fitting. The compression between the flared tubing and the fitting creates a leak-tight seal.
- Installation: Require specialized tools to flare the tubing, which can add complexity to the installation process.
- Applications: Well-suited for high-pressure applications, such as those found in aerospace, racing, and heavy-duty machinery.
- Advantages: Robust and reliable, capable of handling high pressures and vibrations.
- Disadvantages: More complex installation process due to the need for flaring tools.
Flareless Fittings (Compression Fittings):
- Sealing Mechanism: Utilize a compression ring (ferrule) that deforms the tubing slightly when tightened, creating a leak-proof seal.
- Installation: Generally easier and quicker to install than flared fittings as they do not require specialized flaring tools.
- Applications: Widely used in various applications, including automotive, industrial, and general plumbing.
- Advantages: Easier to install and disassemble, often more cost-effective.
- Disadvantages: May not be suitable for extremely high-pressure applications or those with significant vibration.
Here are the key differences between flare fittings vs flareless in the following:
| Feature | Flared Fittings | Flareless Fittings |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Mechanism | Flared tubing end | Compression ring (ferrule) |
| Installation | Requires flaring tools | Easier to install, no flaring required |
| Pressure Capability | Generally higher pressure capability | May have limitations in very high-pressure applications |
| Vibration Resistance | Generally higher vibration resistance | May have limitations in high-vibration environments |
| Ease of Installation | More complex installation | Easier and quicker installation |
The choice between flared and flareless fittings depends on several factors, including the specific application, pressure requirements, vibration levels, and ease of installation and maintenance.
Factors About How to Select Flare Fittings
1. Application:
- Industry: What industry are you working in? (e.g., automotive, aerospace, industrial, marine)
- Specific Application: What is the exact purpose of the fluid system? (e.g., brake lines, fuel lines, hydraulic systems, refrigeration)
- Operating Conditions:
- Pressure: What is the maximum operating pressure of the system?
- Temperature: Will the fittings be exposed to high or low temperatures?
- Vibration: Is the system subject to significant vibration?
- Corrosion: Will the fittings be exposed to corrosive environments?
2. Fluid Type:
- Compatibility: Is the fitting material compatible with the fluid being transported? (e.g., compatibility with gasoline, oil, hydraulic fluids, refrigerants)
- Chemical Properties: Are there any corrosive or reactive properties of the fluid that need to be considered?
3. Pressure Requirements:
- Maximum Operating Pressure: The fitting must be able to withstand the maximum pressure within the system without leaking or failing.
- Pressure Fluctuations: Will the system experience significant pressure fluctuations?
4. Vibration and Shock:
- Vibration Levels: Will the system be subjected to high levels of vibration?
- Shock Loads: Will the system experience sudden shocks or impacts?
5. Temperature Range:
- Operating Temperature: What is the expected temperature range during operation?
- Extreme Temperatures: Will the fittings be exposed to extreme temperatures (e.g., very hot or very cold)?
6. Corrosion Resistance:
- Environment: Will the fittings be exposed to corrosive environments (e.g., salt spray, chemicals)?
- Material Selection: Choose materials that are resistant to corrosion in the specific environment.
7. Installation and Maintenance:
- Ease of Installation: Consider the ease of installation and maintenance, especially if frequent disassembly and reassembly are required.
- Accessibility: How accessible are the fittings for installation, inspection, and maintenance?
8. Cost Considerations:
- Budget: Determine the budget available for the fittings.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Consider the long-term cost-effectiveness of different fitting options, including factors such as durability, maintenance requirements, and potential for leaks.
9. Industry Standards:
- Compliance: Ensure that the chosen fittings comply with relevant industry standards and regulations (e.g., SAE, ISO).
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the most appropriate flare fittings for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance, safety, and reliability.
Flare Fitting Industry Standards and Compliance
Flare fittings are subject to various industry standards that ensure compatibility, quality, and safety. Some of the most prominent standards include:
SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) Standards:
- SAE plays a crucial role in developing and maintaining standards for automotive and aerospace industries, including flare fittings.
- SAE J514: Covers 37-degree flare fittings, commonly referred to as JIC fittings. This standard outlines dimensions, tolerances, and performance requirements for these fittings.
- Other SAE standards address specific aspects like materials, testing procedures, and quality control for flare fittings.
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) Standards:
- ISO develops international standards for various industries, including fluid power.
- ISO 8434: Specifies requirements for metallic tube connections, including 24-degree flareless and 37-degree flare fittings.
- ISO 2974: Defines the dimensions and performance requirements for 24-degree cone fittings (flare fittings) used in hydraulic systems.
Other Relevant Standards:
- Military Standards: In aerospace and defense applications, military standards like MIL-DTL-18866 may apply to flare fittings.
- Industry-Specific Standards: Some industries may have specific standards or guidelines for flare fittings used in their particular applications.
Compliance with these standards is crucial for:
- Ensuring interchangeability: Fittings that comply with the same standards are more likely to be compatible with each other, even from different manufacturers.
- Maintaining quality and safety: Adherence to standards ensures that fittings meet specific performance requirements, such as pressure ratings, leak tightness, and resistance to fatigue.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In many industries, compliance with specific standards is required to meet regulatory requirements and ensure product safety.
By adhering to these industry standards, manufacturers can produce high-quality, reliable flare fittings that meet the demands of various applications.
Conclusion
Selecting the right type of flare fitting is crucial for the success of any fluid system. By understanding the characteristics, advantages, and limitations of different types, such as AN, JIC, 45-degree, and inverted flare fittings, you can make informed decisions that optimize performance, enhance safety, and ensure the longevity of your system.
Whether you’re working on an automotive project, building a custom hydraulic system, or involved in industrial applications, the information in this guide will empower you to choose the most suitable flare fittings for your specific needs.
Ready to upgrade your fluid system with high-quality flare fittings? Contact us today to learn more about our extensive selection of flare fittings, including AN, JIC, and inverted flare options. As a leading manufacturer, we provide top-quality fittings at competitive wholesale prices.



