The “R vs RC Thread” debate centers on the distinctions between rigid conduit (R) and rigid PVC conduit (RC). These electrical conduits, while serving the same basic purpose, differ significantly in materials and applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for safe and compliant electrical installations.
This blog post explores the key variations between R and RC thread types, covering their material composition, durability, installation considerations, and appropriate usage scenarios. We’ll clarify when to choose one over the other, ensuring you make informed decisions for your electrical projects.
What Is R Thread
The R thread, specifically the BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) external thread, is a crucial component in systems demanding robust connections. Its defining characteristic is its conical shape. This taper, where the diameter decreases along the thread’s length, is fundamental to its functionality.
This tapered design allows the R thread to create a seal through mechanical interference. As the fitting is tightened into a corresponding female thread, the tapering forces the threads to bind together, effectively sealing the joint and preventing leaks. This makes R threads suitable for applications requiring high-pressure sealing.
What Is RC Thread
RC threads, defined as BSPT internal threads, are characterized by their tapered design. Specifically, they are engineered to mate with R-type external threads, creating a secure connection. The unique thread profile of Rc threads allows for a tight seal when engaged with their male counterparts. This design is crucial for preventing leaks, particularly in hydraulic systems where high pressure is a factor.
R vs RC Thread
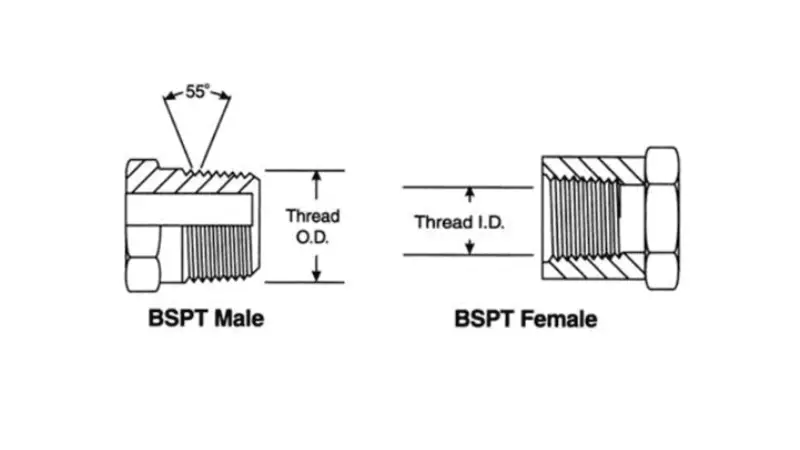
When dealing with fluid power systems, accurate thread identification is paramount. R and RC threads, both belonging to the British Standard Pipe Taper (BSPT) family, play crucial roles among the various thread types encountered. However, their distinct characteristics and applications necessitate a clear understanding of their differences. These tapered threads are designed to create pressure-tight seals, which is vital in industries reliant on hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
The importance of distinguishing between R and RC threads stems from the potential for leaks and system failures when incorrect connections are made. While both are tapered, one is external, and the other internal, leading to very different applications.
Therefore, a precise understanding of each thread type’s function and features is essential for ensuring system integrity and optimal performance.
BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper):
- Both R and RC threads fall under the BSPT standard, meaning they share a 55-degree thread angle. This is a crucial distinction from NPT (National Pipe Thread), which has a 60-degree angle. This difference makes them incompatible.
- The taper in BSPT threads is designed to create a mechanical seal. As the threads are tightened, they compress against each other, leading to a progressively tighter fit.
- However, even with the tapered design, thread sealants are often used to ensure a reliable, leak-free connection, especially in high-pressure applications.
R Threads (External):
- These are the male counterparts in BSPT connections.
- The external taper allows them to wedge into the internal RC threads, generating the sealing force.
- Applications: Commonly found on pipe ends, fittings, and valves.
RC Threads (Internal):
- These are the female counterparts, designed to receive R threads.
- The internal taper matches the R thread, facilitating the compression and sealing process.
- Applications: Found in the internal threads of fittings, valve bodies, and equipment ports.
Key Differences and Nuances:
Sealing Mechanism:
- While both rely on thread interference, the interaction between the external R thread and the internal RC thread is what creates the final seal. The precision of the taper is essential for this.
- In high-pressure systems, the RC thread’s design often provides a more secure seal due to the way it compresses the external R thread.
Applications:
- R threads are used in a wide range of industrial and plumbing applications.
- RC threads are particularly favored in high-pressure hydraulic and pneumatic systems, where leakage prevention is critical.
- Industries like oil and gas, manufacturing, and heavy equipment rely heavily on these types of thread connections.
Expanded Comparison Chart between R threads and RC in the following:
| Feature | R Threads (External) | RC Threads (Internal) |
| Standard | BSPT | BSPT |
| Thread Type | Tapered | Tapered |
| Gender | Male | Female |
| Function | Provides external threaded connection | Receives external threaded connection |
| Sealing | Thread interference, often with sealant | Thread interference, enhanced sealing in high-pressure applications |
| Applications | Pipes, fittings, valves | Fittings, valve bodies, equipment ports |
| Pressure use | Moderate to high pressure applications. | High pressure applications. |
Important Considerations:
- Proper installation is crucial for both R and RC threads. Overtightening can damage the threads and lead to leaks.
- Using the correct thread sealant is essential for ensuring a reliable seal.
- When working with high-pressure systems, selecting fittings and components rated for the intended pressure is vital.
How to Choose R Threads and RC Threads
Choosing the correct R and RC threads is crucial for ensuring leak-free and reliable connections in various fluid systems. Here’s how to make the right selection:
1. Understand the Application:
Pressure Requirements:
- High-pressure applications, such as hydraulic systems, often favor RC threads due to their enhanced sealing capabilities.
- Lower-pressure applications, like general plumbing, may use R threads.
Fluid Type:
The type of fluid being conveyed (e.g., water, oil, gas) can influence the selection. Some fluids may require specific sealant compatibility.
Environment:
Consider the operating environment, including temperature, vibration, and potential exposure to corrosive substances.
2. Identify the Connection Type:
Male vs. Female:
R threads are always male (external), and RC threads are always female (internal). Ensure that the chosen threads correspond to the required connection type.
Matching Threads:
R threads are designed to mate with RC threads. Therefore, when selecting one, the other must also be used.
3. Consider the Thread Standard:
BSPT:
Both R and RC threads fall under the BSPT standard. Ensure that all components adhere to this standard for compatibility.
4. Pay Attention to Installation:
Proper Alignment:
- Ensure that the threads are properly aligned during installation to prevent cross-threading.
Torque Specifications:
Follow the correct torque specifications to avoid over-tightening or under-tightening, both of which can compromise the seal.
Sealant Use:
Use an appropriate thread sealant to enhance the seal, especially in high-pressure applications.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the appropriate R and RC threads for your specific application, ensuring reliable and leak-free connections.
Conclusion
In essence, the distinction between R and RC threads lies in their taper and sealing mechanisms. R threads, being parallel, rely on mechanical seals, while RC threads, tapered, achieve sealing through thread interference. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate fittings for hydraulic systems, ensuring leak-free and efficient operation.
Proper thread selection directly impacts system integrity and performance. Using the wrong thread type can lead to leaks, pressure loss, and potential system failure. Therefore, careful consideration of the application and required sealing method is paramount.
For reliable, high-quality wholesale fittings, explore the extensive range offered by DF Hydraulics. Visit us now to find the perfect solution for your hydraulic needs.



