Hydraulic systems rely heavily on fittings to connect components and ensure fluid flow without leaks. Understanding the working pressure of these fittings is crucial for system safety and efficiency.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the factors that influence fitting pressure ratings, explore different types of fittings and their pressure capabilities, and provide practical tips for selecting the right fittings for your specific application.
We’ll also discuss the importance of regular inspection and maintenance to prevent failures and ensure optimal system performance. Whether you’re a seasoned hydraulics professional or a curious enthusiast, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to confidently select and utilize hydraulic fittings that can withstand the pressures of your system.
What is Hydraulic Fitting Working Pressure
Hydraulic fitting working pressure refers to the maximum pressure that a hydraulic fitting can withstand without failing. This pressure rating is a critical factor in the design and operation of any hydraulic system.
Fittings are used to connect various components within a hydraulic system, such as hoses, pipes, and valves. They are subjected to significant internal pressure when the system is operating. If the working pressure of the system exceeds the pressure rating of the fitting, it can lead to catastrophic failures, including leaks, ruptures, and even explosions. These failures can result in serious injuries, equipment damage, and costly downtime.
Hydraulic Fitting Pressure Rating

Hydraulic fitting pressure ratings are crucial for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of any hydraulic system. These ratings indicate the maximum pressure that a fitting can withstand without failing or leaking.
Factors Influencing Pressure Ratings:
- Material: The material of the fitting significantly impacts its pressure rating. Stronger materials like high-strength steel and stainless steel can withstand higher pressures compared to brass or aluminum.
- Design: The design of the fitting, including its shape, size, and thread type, plays a vital role.
- Manufacturing Process: The quality of the manufacturing process, including the precision of machining and the integrity of the material, directly affects the fitting’s strength.
- Operating Conditions: Factors such as temperature extremes, vibration, and exposure to corrosive environments can influence the actual working pressure of a fitting.
Importance of Pressure Ratings:
- Safety: Using fittings with inadequate pressure ratings can lead to catastrophic failures, such as leaks, ruptures, and explosions, potentially causing serious injuries or equipment damage.
- System Reliability: Overloading fittings can cause premature wear and tear, leading to frequent maintenance issues and system downtime.
- System Performance: Properly selected fittings ensure optimal system performance by maintaining consistent fluid flow and preventing pressure drops.
Selecting the Right Hydraulic Fittings:
- Determine System Requirements: Carefully assess the maximum operating pressure of your hydraulic system.
- Consult Our hydraulic fitting manufacturer specifications: Always refer to the manufacturer‘s specifications for the pressure rating of each fitting.
- Consider a Safety Factor: It’s generally recommended to select fittings with a pressure rating significantly higher than the expected system pressure to provide a safety margin.
- Inspect Fittings Regularly: Regularly inspect fittings for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Replace any damaged fittings immediately.
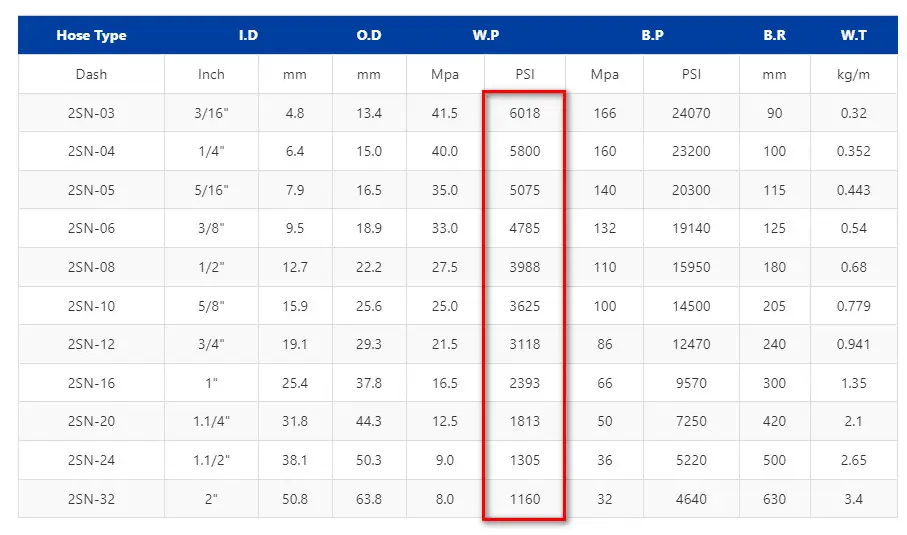
Example of Typical Pressure Ratings for Common Fitting Materials
| Material | Typical Pressure Rating (PSI) |
|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | 6,000 – 10,000 |
| Stainless Steel | 10,000 – 20,000 |
| Brass | 3,000 – 5,000 |
| Aluminum | 2,000 – 4,000 |
Note: This table provides a general overview. Actual pressure ratings can vary significantly depending on the specific fitting design, size, and manufacturer.
Factors Affecting Hydraulic Fitting Working Pressure
Several factors influence the working pressure of a hydraulic fitting:
Material:
- Strength: The inherent strength of the material used to manufacture the fitting is paramount. Stronger materials like high-strength steel and stainless steel can withstand significantly higher pressures than softer materials like brass or aluminum.
- Corrosion Resistance: The material’s resistance to corrosion from the hydraulic fluid is crucial. Corrosion weakens the fitting, reducing its pressure-bearing capacity.
Design and Construction:
- Shape and Size: The geometry of the fitting, including its size, shape, and wall thickness, significantly impacts its strength.
- Thread Type: The type of thread (e.g., NPT, BSP) and its quality significantly influence the fitting’s ability to withstand pressure.
- Sealing Mechanism: The design of the sealing mechanism (e.g., O-rings, gaskets) is critical for preventing leaks and maintaining pressure integrity.
Manufacturing Process:
- Quality Control: The quality of the manufacturing process, including the precision of machining, heat treatment (if applicable), and surface finishing, directly affects the fitting’s strength and reliability.
- Material Defects: Any defects in the material, such as cracks or inclusions, can significantly reduce the fitting’s pressure-bearing capacity.
Operating Conditions:
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures (both high and low) can affect the material properties of the fitting, potentially weakening it.
- Vibration: Constant vibration can induce fatigue in the fitting material, leading to cracks and eventual failure.
- Pressure Surges: Sudden pressure spikes (pressure surges) can exceed the fitting’s design limits, causing damage or failure.
- Fluid Compatibility: The compatibility of the hydraulic fluid with the fitting material is essential. Some fluids can cause corrosion or other forms of degradation.
Installation and Maintenance:
- Proper Installation: Improper installation, such as over-tightening or cross-threading, can damage the fitting and reduce its pressure rating.
- Regular Inspection: Regular inspection of fittings for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage is crucial for identifying potential problems before they lead to failure.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers and technicians can select and install hydraulic fittings that are appropriate for the specific application and operating conditions, ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the hydraulic system.
Conclusion
Understanding hydraulic fitting working pressure is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of your hydraulic systems. By carefully selecting fittings with appropriate pressure ratings and adhering to proper installation practices, you can minimize the risk of leaks, failures, and costly downtime.
Ready to upgrade your hydraulic system with high-quality, reliable fittings? [Our Hydraulic Manufacturer] offers a wide range of wholesale hydraulic fittings designed to meet the most demanding applications. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and receive a customized quote. Visit our website at dfhydraulics.com to explore our full product catalog.



