When working with hydraulic fittings, understanding thread standards is crucial for ensuring proper installation and sealing. British Thread vs NPT is a frequent comparison in industries like plumbing, hydraulics, and automotive.
While both are used to connect pipes and fittings, they differ in design, sealing mechanisms, and applications. In this article, we’ll break down these differences in detail and help you determine which is best suited for your needs.
What is British Thread?
British threads are based on a variety of standards, including the BSP (British Standard Pipe) and BSPT (British Standard Pipe Tapered) threads. These threads are widely used in the UK and several other countries.
British Thread refers to a set of thread profiles used primarily in pipe fittings. The most common types are BSP and BSPT, which are used in fluid and gas transmission systems. The BSP standard includes two types: parallel (BSPP) and tapered (BSPT).
The British Thread system originated to standardize the fittings used in industrial piping systems, making them safer and more consistent. These standards are now used globally, especially in regions that follow British engineering and manufacturing practices.
Standards:
- BSPP (British Standard Parallel): Used for applications where a sealing washer or O-ring is used.
- BSPT (British Standard Tapered): Tapered threads that form a seal when tightened.
Classification:
| Type | Profile | Purpose | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| BSPP | Parallel | Non-tapered, sealing via O-ring | Pipe fittings in Europe and UK |
| BSPT | Tapered | Self-sealing through thread contact | Heavy-duty industrial systems |
What is NPT Thread?
The National Pipe Thread (NPT) standard is primarily used in the United States and is recognized globally for specific applications in various industries, such as hydraulics, plumbing, and gas systems.
NPT threads are designed to create a tight seal by allowing the male and female threads to form a seal when tightened. The NPT standard is specifically intended for fluid-tight and gas-tight fittings.
NPT originated in the US to standardize pipe threads for fluid and gas transfer. It is widely adopted in the US and parts of Canada, as well as many industrial applications globally.
Standards:
- NPT: A tapered thread standard used for creating a tight seal in pipes and fittings.
- NPS (National Pipe Straight): A straight-thread version of NPT used for mechanical and pressure-tight seals.
Classification:
| Type | Profile | Purpose | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| NPT | Tapered | Self-sealing, primarily for fluids and gases | Predominantly used in the US |
| NPS | Straight | For non-sealing mechanical joints | Mechanical connections |
British Thread VS NPT
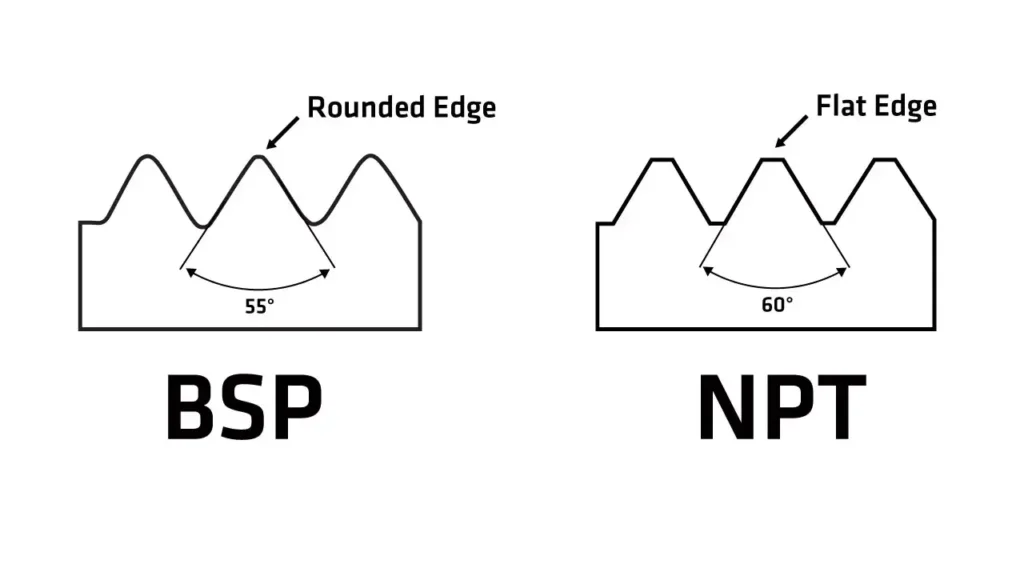
Design Differences:
- Thread Profile:
- British Thread: BSP threads are parallel (BSPP) or tapered (BSPT), with BSPT having a conical shape.
- NPT: Always tapered, with a conical shape, designed for sealing under pressure.
Sealing Mechanisms:
- British Thread: BSPT relies on the angle of the tapered threads to create a seal, while BSPP requires additional sealing mechanisms like O-rings.
- NPT: The tapered threads create a tight seal by compression as the fitting is tightened.
Sizes and Compatibility:
- British Thread: BSP threads are available in a wider variety of sizes and are often used in European systems.
- NPT: NPT threads are also available in various sizes but are predominantly used in the US and are not always compatible with BSP fittings due to differing thread angles.
Materials:
Both thread types can be made from materials such as steel, stainless steel, and brass. However, NPT threads are more commonly used in the US, whereas BSP is more frequently used in European applications.
Applications:
- British Thread: Common in UK, Europe, and Commonwealth countries for fluid and gas transfer in industrial settings.
- NPT: Primarily used in the US for fluid, gas, and air transfer applications.
Structure and Installation:
- British Thread: BSPT threads taper to a 1:16 ratio. BSPP fittings require O-rings for sealing.
- NPT: NPT threads taper at a 1:16 angle, creating a pressure-tight seal when twisted.
Sealing:
- British Thread: BSPT creates a seal when the threads come into contact; BSPP uses an additional O-ring.
- NPT: The conical threads provide a seal by compression, ensuring a leak-tight connection.
| Feature/Aspect | British Thread (BSP) | NPT |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Type | Parallel (BSPP) or tapered (BSPT) | Always tapered |
| Sealing Mechanism | BSPT relies on thread angle; BSPP requires O-rings | Compression of tapered threads for sealing |
| Sizes & Compatibility | Various sizes, commonly used in European systems; not always compatible with NPT | Various sizes, predominantly used in the US; incompatible with BSP due to different angles |
| Materials | BSPT tapers at a 1:16 ratio; BSPP uses O-rings for sealing | Steel, stainless steel, brass; more common in American applications |
| Applications | UK, Europe, and Commonwealth countries for fluid/gas transfer | US for fluid, gas, and air transfer |
| Structure & Installation | Tapers at a 1:16 ratio, creates a pressure-tight seal when tightened | Tapers at a 1:16 ratio, create a pressure-tight seal when tightened |

How to Choose Between British Thread and NPT?
Choosing between British Standard Pipe (BSP) threads and National Pipe Thread (NPT) depends heavily on the application and the region where the equipment will be used.
Both thread types are used for fluid and gas transfer, but they are not interchangeable due to differences in thread form and sealing mechanisms. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for ensuring leak-free connections and system compatibility.
Regional Standards:
- NPT is predominantly used in North America.
- BSP is common in Europe, Asia, Australia, and other regions that adhere to British standards.
Thread Form and Sealing:
- NPT threads are tapered, relying on thread interference for sealing.
- BSP threads can be either tapered (BSPT) or parallel (BSPP). BSPT seals through thread interference, while BSPP requires a separate sealing element (O-ring, gasket).
Application Requirements:
- Consider the pressure and temperature requirements of the system.
- Evaluate the need for frequent assembly and disassembly.
- Determine the type of fluid or gas being conveyed.
Therefore, selecting between BSP and NPT requires careful consideration of regional standards, thread form, sealing requirements, and application-specific needs. Always verify the thread type required by your equipment and ensure compatibility to avoid costly leaks and system failures.
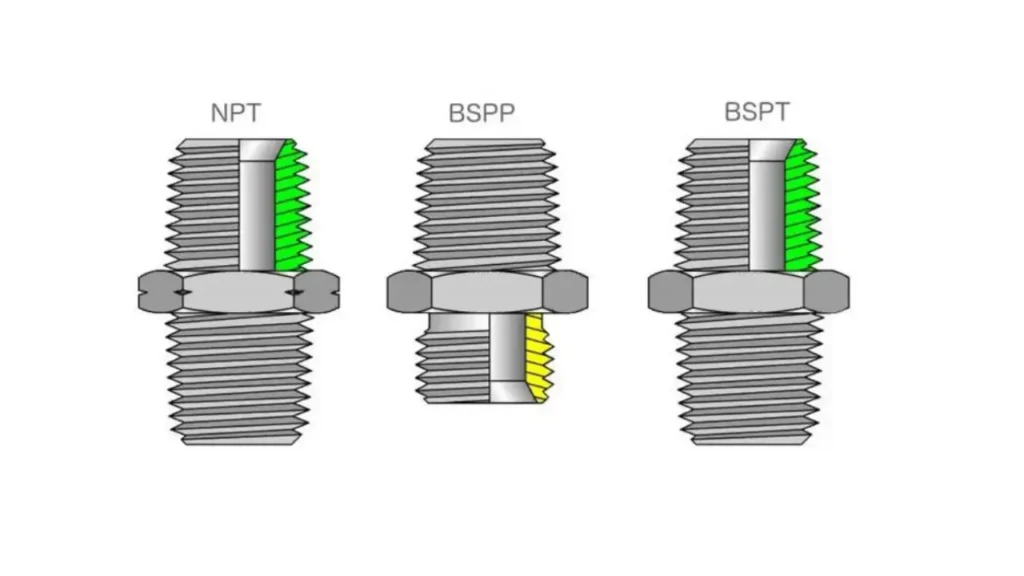
Important Considerations:
- Thread Compatibility: BSP and NPT threads are not interchangeable. Always check the thread type before installation.
- Sealing Requirements: BSPP requires O-rings, while NPT threads rely on tight compression.
- Material Selection: Make sure that the materials used are suitable for the application, especially when handling gases or fluids at high pressure.
Conclusion:
The British Thread vs NPT comparison boils down to regional standards, application requirements, and thread design. NPT threads are preferred for high-pressure and gas-tight applications, whereas BSP threads are commonly used in Europe and other regions.
Understanding these differences will help ensure that you select the right fitting for your system. If you’re unsure or need custom fittings, feel free to contact us at Dingfeng, where we offer a wide range of high-quality fittings to meet your needs.
FAQs About British Thread VS NPT
Are NPT and BSP threads compatible?
No, NPT and BSP threads are not compatible due to differences in thread angles and designs. Using mismatched threads can cause leaks and installation issues. Always ensure you’re using the correct fitting type.
How do I know if my thread is NPT or BSP?
The best way to identify the thread is by measuring the angle of the thread. NPT has a 60-degree thread angle, while BSP has a 55-degree angle. Additionally, BSP is parallel or tapered, while NPT is only tapered.
Can NPT and BSPT be used together?
No, NPT and BSPT should not be used together. The different thread angles and designs will prevent a proper seal from forming, leading to leaks.
Is 1/2 BSP the same as 1/2 NPT?
No, 1/2 BSP and 1/2 NPT are different. The thread profiles, angles, and sealing mechanisms differ, which means they cannot be interchanged.
What materials are suitable for NPT and BSP fittings?
Both NPT and BSP fittings are available in materials like steel, stainless steel, and brass. The choice of material should depend on the application’s pressure, temperature, and corrosive factors.
Where can I buy hydraulic fittings?
For customized fittings, look no further than DF Hydraulics. We offer a full range of British and NPT fittings, and we can design and manufacture fittings to your exact specifications. Feel free to contact us directly to discuss your needs.



