Choosing the right type of thread for your plumbing, hydraulic, or pneumatic system is crucial for ensuring proper function and safety. Two common thread standards you’ll encounter are BSP (British Standard Pipe) and NPT (National Pipe Thread). While both are used in fluid handling systems, they have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications.
This blog post will delve into the key differences between BSP and NPT threads, including their thread profiles, sealing mechanisms, and typical applications. By understanding these distinctions, you can make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate thread type for your specific needs.
What Is BSP?
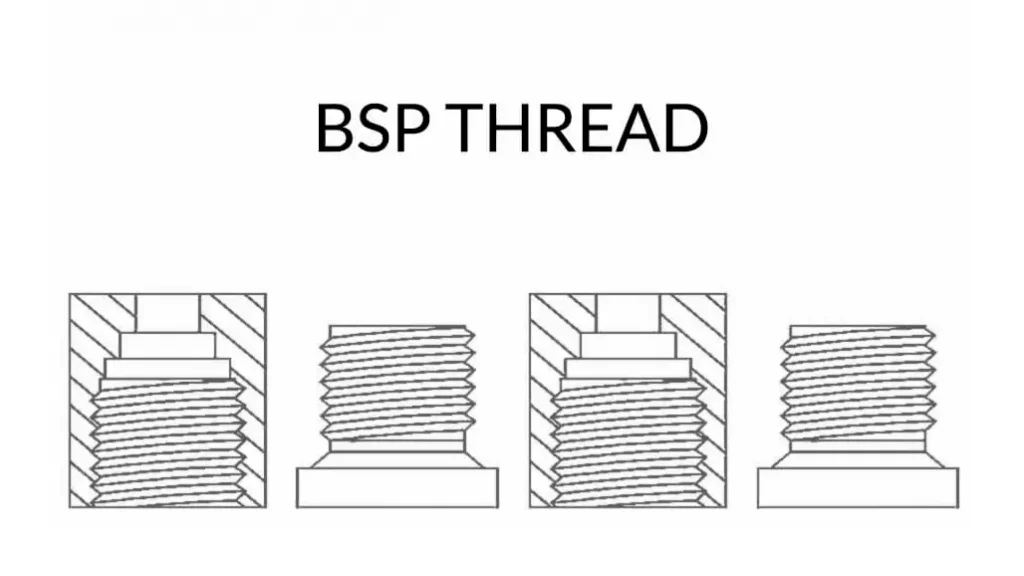
BSP stands for “British Standard Pipe.” It’s a set of technical standards for screw threads used in plumbing, hydraulics, and pneumatic systems.
BSP encompasses two main types of threads:
- BSPT (British Standard Pipe Tapered): These threads have a tapered profile, meaning the diameter of the male thread gradually increases along its length. The seal is achieved primarily through this taper, which creates a tight fit when screwed into the female counterpart.
- BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel): These threads have a parallel profile, meaning the diameter of the male thread remains constant throughout its length. Sealing is achieved through the use of separate sealing components, such as washers or O-rings.
BSP threads are widely used in various applications due to their strength, reliability, and compatibility with a wide range of fittings and components.
BSP Thread Size Chart
| BSP Size | Nominal Diameter (inches) | Threads per Inch (TPI) |
|---|---|---|
| 1/16″ | 0.136 | 28 |
| 1/8″ | 0.383 | 28 |
| 1/4″ | 0.518 | 19 |
| 3/8″ | 0.656 | 19 |
| 1/2″ | 0.825 | 14 |
| 5/8″ | 0.902 | 14 |
| 3/4″ | 1.041 | 14 |
| 7/8″ | 1.189 | 14 |
| 1″ | 1.309 | 11 |
| 1-1/4″ | 1.650 | 11 |
| 1-1/2″ | 1.882 | 11 |
| 2″ | 2.347 | 11 |
Note: This table provides general information. Actual dimensions may vary slightly depending on specific standards and manufacturing tolerances.
What Is NPT?
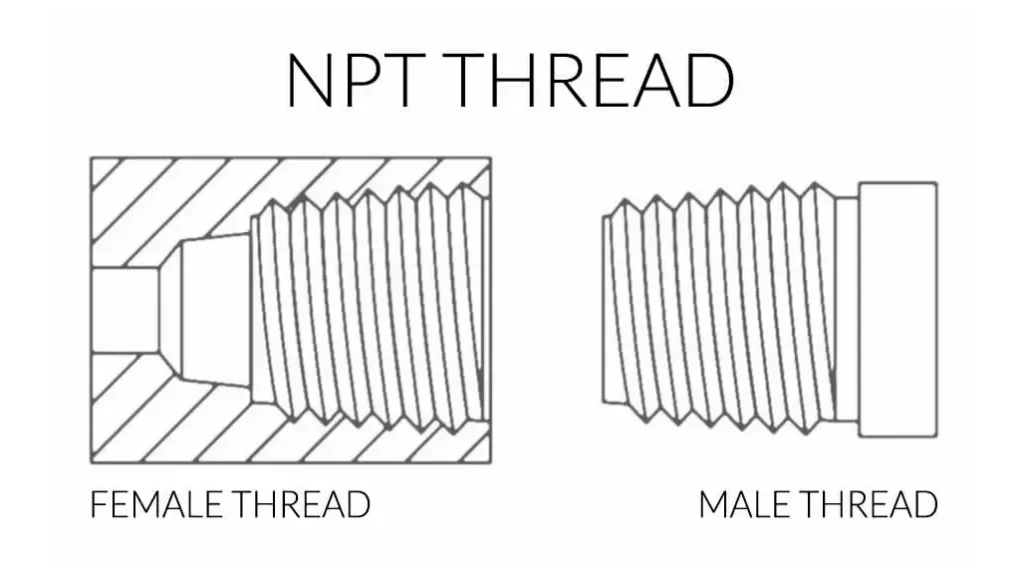
NPT stands for National Pipe Tapered. It’s a standard for tapered pipe threads, primarily used in North America. NPT threads feature a 60-degree thread angle and a slight taper on the male thread. This taper, combined with the use of thread sealants like Teflon tape or pipe dope, creates a tight seal when the male thread is screwed into the female counterpart.
NPT threads are widely used in various applications, including plumbing, hydraulics, and natural gas lines. Their tapered design provides a robust and leak-resistant connection, making them suitable for high-pressure applications and environments where vibration or pressure fluctuations may occur.
NPT Thread Size Chart
| Nominal Pipe Size (NPT) | Threads per Inch (TPI) |
|---|---|
| 1/16″ | 27 |
| 1/8″ | 27 |
| 1/4″ | 18 |
| 3/8″ | 18 |
| 1/2″ | 14 |
| 3/4″ | 14 |
| 1″ | 11 1/2 |
| 1 1/4″ | 11 1/2 |
| 1 1/2″ | 11 1/2 |
| 2″ | 11 1/2 |
Note: This chart provides the most common NPT thread sizes and their corresponding threads per inch (TPI).
BSP vs NPT
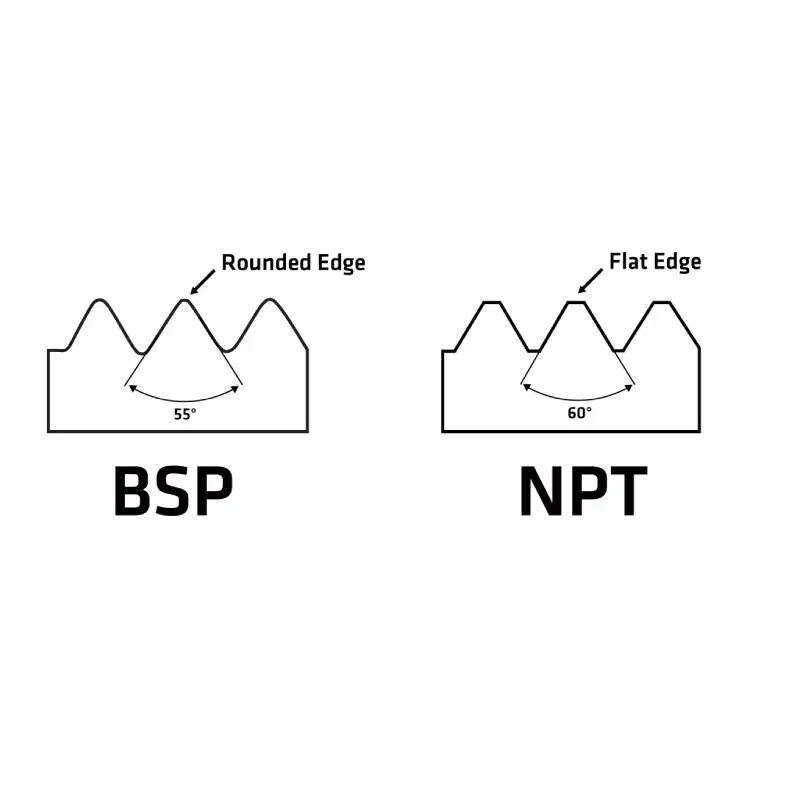
BSP (British Standard Pipe) and NPT (National Pipe Tapered) are both thread standards used in plumbing, hydraulics, and pneumatic systems, but they have key differences:
BSP:
- Thread Profile: Tapered, with a 55-degree thread angle.
- Sealing: Primarily achieved through the taper of the male thread.
- Common Usage: Widely used in Europe and other parts of the world.
NPT:
- Thread Profile: Tapered, with a 60-degree thread angle.
- Sealing: Achieved through a combination of thread taper and the use of thread sealants (e.g., Teflon tape, pipe dope).
- Common Usage: Predominantly used in North America.
This table can show you the difference between NPT and BSP thread
| Feature | BSP | NPT |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Angle | 55 degrees | 60 degrees |
| Sealing Mechanism | Primarily thread taper | Thread taper and sealants |
| Common Usage | Europe and other parts of the world | North America |
Important Note: BSP and NPT threads are not interchangeable. Attempting to connect a BSP fitting to an NPT component or vice versa can result in leaks, damage to the threads, and system failure.
BSP vs NPT Applications
BSP (British Standard Pipe):
Common Applications:
- Plumbing systems (water, gas)
- Hydraulic systems (low to medium pressure)
- Pneumatic systems
- Automotive applications
- Marine applications
- General industrial applications
NPT (National Pipe Tapered):
Common Applications:
- Plumbing systems (water, gas)
- Natural gas pipelines
- Oil and gas industry
- High-pressure hydraulic systems
- Compressed air systems
- Industrial machinery
| Feature | BSP | NPT |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Angle | 55 degrees | 60 degrees |
| Sealing Mechanism | Primarily thread taper | Thread taper and sealants |
| Common Usage | Europe and other parts of the world | North America |
| Common Applications | Plumbing, hydraulics, pneumatics, automotive, marine | Plumbing, natural gas, oil & gas, high-pressure applications |
Important Note: Specific applications may vary depending on the industry, pressure requirements, and other factors.
BSP vs NPT Standardization
BSP (British Standard Pipe) and NPT (National Pipe Tapered) are two distinct thread standards used in various industries, primarily in plumbing, hydraulics, and pneumatics.
- BSP: Originating in the United Kingdom, BSP threads are characterized by a 55-degree thread angle and a tapered profile. Sealing is primarily achieved through the taper of the male thread, which creates a tight fit when screwed into the female counterpart. BSP threads are widely used in Europe and other parts of the world.
- NPT: Developed in the United States, NPT threads feature a 60-degree thread angle and a tapered profile. Sealing is achieved through a combination of the thread taper and the application of thread sealants such as Teflon tape or pipe dope. NPT threads are predominantly used in North America.
| Feature | BSP | NPT |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Angle | 55 degrees | 60 degrees |
| Sealing Mechanism | Primarily thread taper | Thread taper and sealants |
| Common Usage | Europe and other parts of the world | North America |
| Common Applications | Plumbing, hydraulics, pneumatics, automotive, marine | Plumbing, natural gas, oil & gas, high-pressure applications |
| Standardization | ISO 228-1 (G threads) | ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 |
This updated table now includes the relevant standardization bodies for each thread type:
- BSP: Standardized under ISO 228-1 (G threads).
- NPT: Standardized under ANSI/ASME B1.20.1.
BSP and NPT Thread Chart
BSP (British Standard Pipe) and NPT (National Pipe Tapered) are two common thread standards used in various industries, particularly plumbing and hydraulics. They have distinct characteristics:
BSP:
- Thread Angle: 55 degrees
- Sealing: Primarily achieved through the taper of the male thread.
- Common Usage: Widely used in Europe and other parts of the world.
- Standardization: ISO 228-1 (G threads)
NPT:
- Thread Angle: 60 degrees
- Sealing: Achieved through a combination of thread taper and sealants (e.g., Teflon tape, pipe dope).
- Common Usage: Predominantly used in North America.
- Standardization: ANSI/ASME B1.20.1
Key Differences BSP and NPT thread
| Feature | BSP | NPT |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Angle | 55 degrees | 60 degrees |
| Sealing Mechanism | Primarily thread taper | Thread taper and sealants |
| Common Usage | Europe and other parts of the world | North America |
| Standardization | ISO 228-1 (G threads) | ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 |
Important Noted: BSP and NPT threads are not interchangeable. Using incompatible fittings can lead to leaks, damage, and system failure.
Are BSP and NPT Compatible?
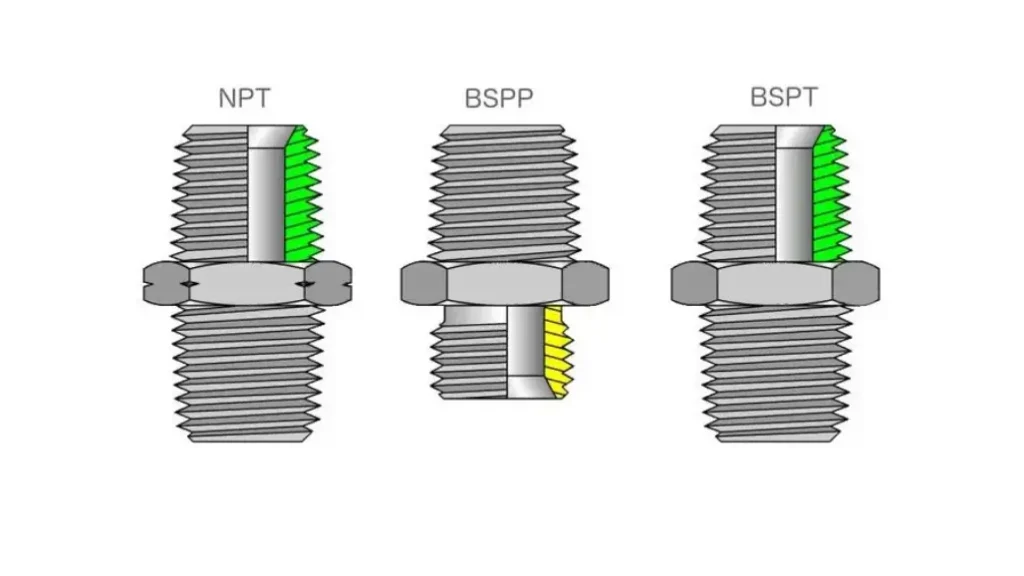
No, BSP and NPT threads are not compatible.
BSP (British Standard Pipe) and NPT (National Pipe Tapered) have different thread angles (55 degrees for BSP and 60 degrees for NPT), thread pitches, and sealing mechanisms. Attempting to connect a BSP fitting to an NPT component, or vice versa, can result in:
Leaks: The mismatched threads will not create a proper seal, leading to fluid leakage.
Cross-threading: The threads may not align correctly, causing damage to the threads themselves.
System Failure: In critical applications, incompatible threads can lead to system malfunctions and potential safety hazards.
It is crucial to always use fittings and components with matching thread standards to ensure proper function and prevent issues.
How Do You Know if a thread is BSP or NPT?
Identifying whether a thread is BSP or NPT involves a combination of visual inspection and understanding their key differences.
Thread Profile: BSP threads are typically parallel, while NPT threads are tapered. Visually inspect the threads to determine if they maintain a consistent diameter or gradually increase in size along their length.
Thread Angle: While subtle, BSP threads have a 55-degree thread angle, whereas NPT threads have a 60-degree angle.
Sealing Method: BSP threads often rely on separate seals like washers or O-rings, while NPT threads primarily rely on the taper of the male thread and the use of thread sealants.
Markings: Look for any markings on the fitting that might indicate the thread type, such as “BSP” or “NPT.”
By carefully examining these characteristics, you can usually determine whether you are dealing with BSP or NPT threads.
Is BSP used in Europe?
Yes, BSP (British Standard Pipe) threads are widely used in Europe. They are a common standard for pipe fittings and hydraulic components across many European countries.
Does Canada use BSP or NPT?
In Canada, NPT (National Pipe Tapered) is the most commonly used thread standard, particularly for plumbing, hydraulics, and other industrial applications.
Which countries use NPT thread?
NPT (National Pipe Tapered) threads are primarily used in the United States, Canada, and many countries in South America.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the key differences between BSP and NPT threads is crucial for selecting the appropriate fittings and ensuring the integrity of your hydraulic or pneumatic systems. BSP threads, with their tapered profile and self-sealing mechanism, are well-suited for general-purpose applications.
NPT threads, on the other hand, offer a robust and leak-tight seal, making them ideal for high-pressure applications and environments where vibration or pressure fluctuations are common.
If you’re seeking high-quality hydraulic fittings, including BSP and NPT options, consider sourcing your components from our hydraulic fitting factory. We offer a wide range of wholesale hydraulic fittings, manufactured to the highest industry standards. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our competitive pricing and exceptional service can benefit your business.