Understanding the distinctions between NPSM and NPTF thread types is crucial for ensuring leak-free and efficient fluid transfer in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. While both are used in various industrial applications, their design and sealing mechanisms differ significantly. This blog aims to clarify these differences, helping you choose the right fittings for your specific needs.
We’ll delve into the unique characteristics of each thread type, exploring their sealing methods, pressure ratings, and typical applications. You’ll gain the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions and prevent costly leaks and system failures by highlighting the key differences.
What Is NPSM Thread
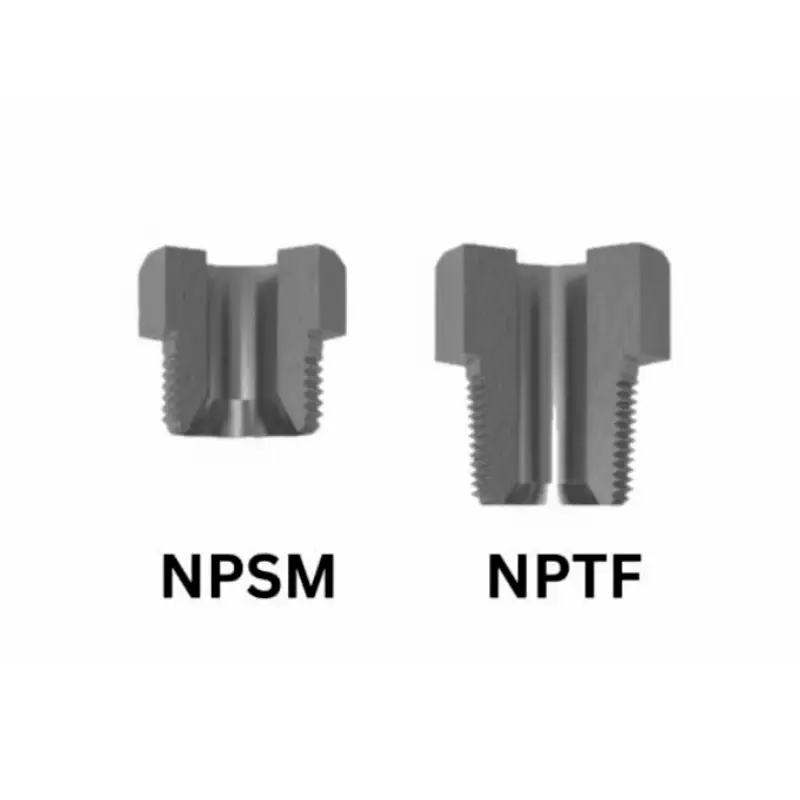
NPSM, which stands for National Pipe Straight Mechanical, is a U.S. standard thread type used in fluid power systems. Unlike tapered pipe threads, NPSM threads are straight, meaning they maintain a constant diameter along their length. This straight thread design necessitates the use of a mechanical seal, such as an O-ring or gasket, to create a leak-free connection.
NPSM threads are commonly found in applications where frequent assembly and disassembly are required, such as in certain hydraulic and pneumatic connections. The mechanical seal provided by an O-ring or gasket allows for easy disconnection and reconnection without damaging the threads or compromising the seal. While effective, NPSM is generally preferred for lower-pressure applications compared to tapered thread types, due to its reliance on external sealing elements.
What Is NPTF Thread



NPTF, or National Pipe Taper Fuel, is a U.S. standard thread type primarily used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems for creating leak-free connections without the need for additional sealants. It’s designed as a “dryseal” thread, meaning the tapered threads themselves crush and deform during tightening, creating a robust, metal-to-metal seal. This tapered design is crucial for achieving a tight, leak-resistant connection in high-pressure applications.
The tapered nature of NPTF threads, combined with their specific pitch and dimensions, allows for a tight fit that effectively seals against fluid or gas leakage. This makes NPTF threads particularly suitable for demanding applications where leaks are unacceptable, such as in fuel, oil, and high-pressure hydraulic systems. The dryseal characteristic of NPTF threads is a key advantage, simplifying assembly and ensuring reliability.
NPSM vs NPTF
NPSM and NPTF are both standard thread types used in fluid power systems, but they differ significantly in their design and application. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate fittings for your hydraulic or pneumatic systems.
Thread Design and Sealing Mechanism
NPTF threads are tapered, meaning their diameter decreases along their length. This tapered design allows the threads to crush and deform during tightening, creating a metal-to-metal seal without the need for additional sealants. This “dryseal” characteristic is essential for high-pressure applications where leaks are unacceptable. The tapered nature of NPTF threads ensures a tight fit, effectively preventing fluid or gas leakage.
NPSM threads, on the other hand, are straight, maintaining a constant diameter along their length. This straight thread design necessitates the use of a mechanical seal, such as an O-ring or gasket, to create a leak-free connection. The seal is formed by an external component, not by the threads themselves. This mechanical seal allows for easier assembly and disassembly, making NPSM suitable for applications where frequent connections are required.
Application and Pressure Ratings
NPTF threads are commonly used in high-pressure hydraulic and pneumatic systems where a reliable, leak-free seal is critical. Their dryseal design makes them ideal for applications involving fuels, oils, and other fluids under high pressure. These fittings are often found in automotive, industrial, and aerospace applications where system integrity is paramount.
NPSM threads are typically used in lower-pressure applications where frequent assembly and disassembly are required. Their mechanical seal design, relying on O-rings or gaskets, allows for easier connections and disconnections without damaging the threads. These fittings are commonly used in fluid transfer systems, instrumentation, and other applications where a reliable seal is needed but high pressure is not a primary concern.
The key differences between NPSM and NPTF threads
| Feature | NPSM | NPTF |
| Thread Type | Straight | Tapered |
| Sealing Mechanism | Mechanical (O-ring or gasket) | Dryseal (metal-to-metal) |
| Pressure Rating | Lower to medium pressure | High pressure |
| Application | Frequent assembly/disassembly, fluid transfer, instrumentation | High-pressure hydraulic and pneumatic systems, fuel systems |
| Sealant Required | Yes (O-ring or gasket) | No (dryseal) |
How to Choose NPSM and NPTF Threads
Choosing the right thread type, NPSM or NPTF, is crucial for ensuring leak-free and reliable connections in your fluid power systems. Proper selection depends on several factors, including the application’s pressure requirements, fluid type, and maintenance needs.
Pressure Requirements
NPTF threads are designed for high-pressure applications, relying on a tapered thread design that creates a robust, metal-to-metal seal without the need for additional sealants. If your system operates under high pressure, especially in critical applications where leaks are unacceptable, NPTF fittings are the preferred choice. The tapered threads crush and deform during tightening, ensuring a tight, leak-resistant connection.
NPSM threads, on the other hand, are better suited for lower to medium-pressure applications. Their straight thread design necessitates the use of a mechanical seal, such as an O-ring or gasket, to prevent leaks. While effective, this design is generally less reliable under extreme pressures compared to NPTF. Ensure the fitting’s pressure rating meets or exceeds your system’s requirements to prevent leaks and failures.
Application and Maintenance Needs
NPTF threads are commonly used in applications where a reliable, leak-free seal is critical and frequent disassembly is not required. Their dryseal design makes them ideal for systems involving fuels, oils, and other fluids under high pressure. These fittings are often found in automotive, industrial, and aerospace applications where system integrity is paramount.
NPSM threads are typically used in applications where frequent assembly and disassembly are required. Their mechanical seal design, relying on O-rings or gaskets, allows for easier connections and disconnections without damaging the threads. These fittings are commonly used in fluid transfer systems, instrumentation, and other applications where a reliable seal is needed but high pressure is not a primary concern. Consider the frequency of maintenance and component changes when choosing between NPSM and NPTF.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the distinct characteristics of NPSM and NPTF fittings is crucial for ensuring leak-free hydraulic connections. NPTF’s tapered threads provide a robust, dryseal for high-pressure applications, while NPSM’s straight threads, coupled with mechanical seals, are ideal for lower-pressure, frequently disassembled systems. Accurate selection minimizes leaks and optimizes system performance.
The choice between NPTF and NPSM hinges on specific application demands, including pressure ratings and maintenance frequency. NPTF’s superior sealing capabilities make it preferred in critical, high-pressure scenarios. Conversely, NPSM’s ease of assembly and disassembly is advantageous in applications requiring frequent adjustments or replacements.
For high-quality wholesale hydraulic fittings, including both NPTF and NPSM types, tailored to your unique requirements, request a quote from DF Hydraulics today. We offer a comprehensive range of durable and reliable fittings, ensuring secure and efficient hydraulic connections. Get in touch to discuss your needs and benefit from our expert services.