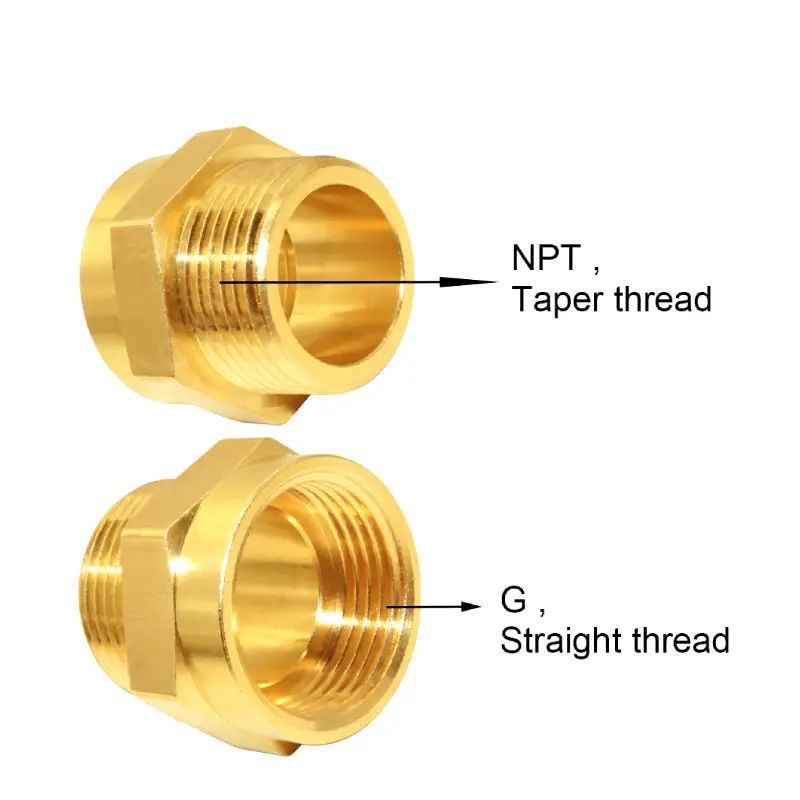
NPT (National Pipe Taper) and G threads are two common types of threaded connections used in various applications, but they have significant differences. NPT threads are tapered, creating a seal as they are tightened. This makes them suitable for many applications, but they may require the use of thread sealant.
G threads, also known as BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel), feature parallel threads. This design requires the use of gaskets or O-rings to create a seal. Understanding the key differences between NPT and G threads is crucial for selecting the appropriate fittings and ensuring proper assembly in your specific application.
What Is NPT Thread
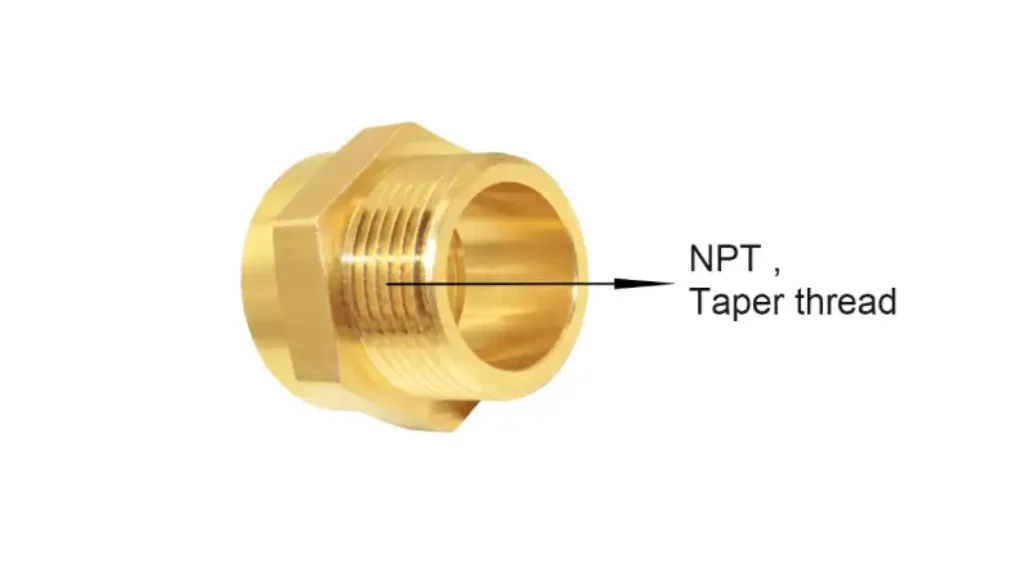

NPT stands for National Pipe Taper. It’s a common standard for tapered threads used in various applications, primarily in plumbing and industrial settings.
NPT threads are characterized by their tapered design. As the male NPT thread is screwed into the female counterpart, the taper forces the threads together, creating a tight compression that effectively seals the connection. This self-sealing mechanism, combined with the use of thread sealants like Teflon tape or pipe dope, makes NPT connections reliable and widely used in many industries.
Recommended products
What Is G Thread
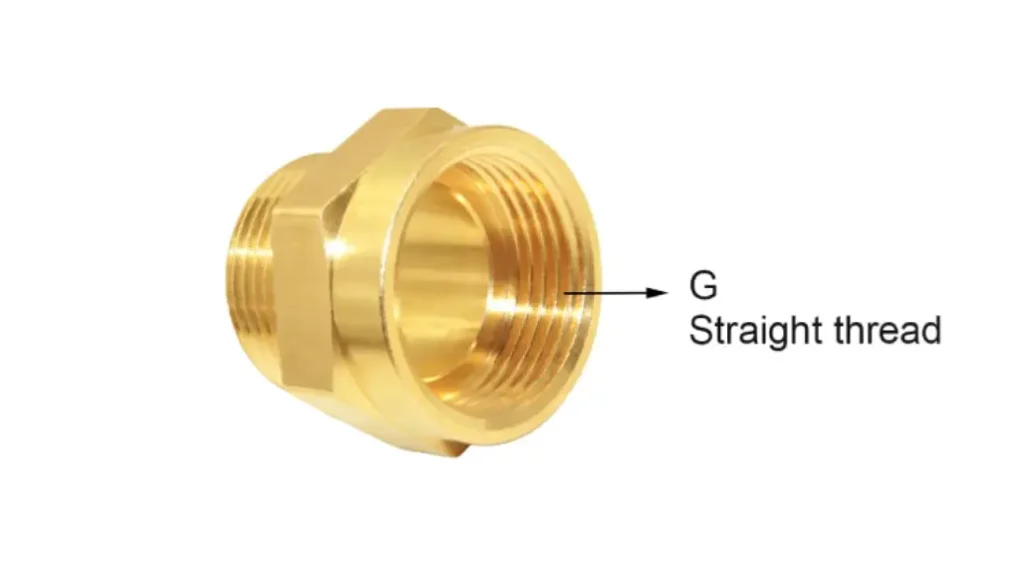

G threads, also known as Whitworth parallel threads, are a type of parallel thread used in various applications, particularly in plumbing and hydraulic systems.
Unlike NPT threads, which rely on a tapered design to create a seal, G threads are parallel, meaning they have a constant diameter along their length. This parallel design requires the use of a separate sealing method, such as gaskets or O-rings, to ensure a leak-proof connection.
G threads are commonly found in applications where the use of thread sealants might be undesirable or impractical.
NPT vs G Thread
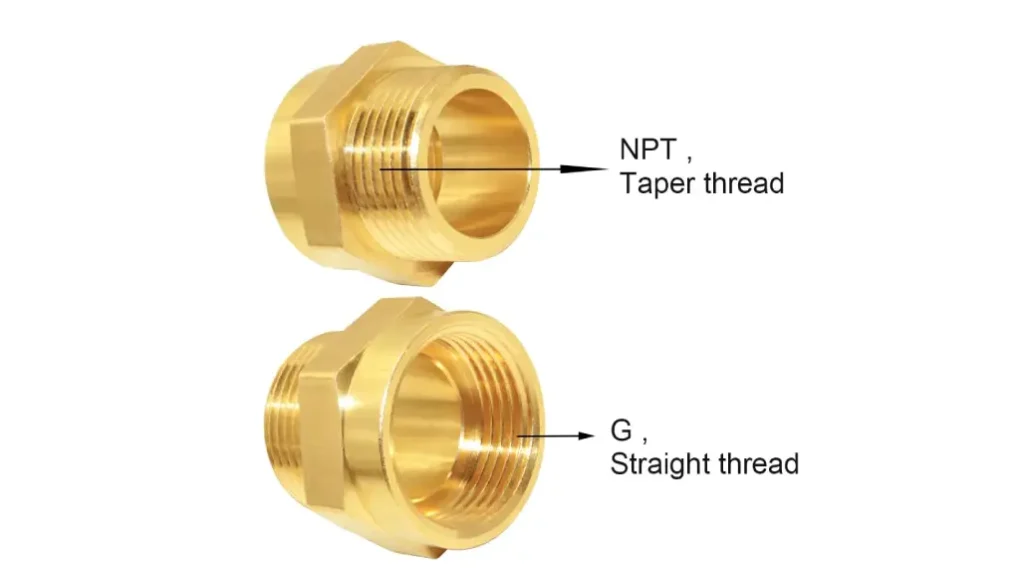
NPT (National Pipe Taper) and G threads are two common thread standards used in various applications, particularly in plumbing and hydraulic systems. While both serve to connect components, they have distinct characteristics:
NPT:
- Tapered: NPT threads have a tapered profile, meaning the diameter of the thread decreases slightly from the base to the tip.
- Sealing Mechanism: The taper creates a seal as the male threads are screwed into the female counterpart. This compression force helps to prevent leaks.
- Sealant Requirement: Typically requires the use of thread sealant (like Teflon tape or pipe dope) to ensure a leak-proof seal.
G Thread:
- Parallel: G threads have a parallel profile, meaning the diameter of the thread remains constant along its length.
- Sealing Mechanism: Relies on a separate sealing method, such as gaskets or O-rings, to create a seal.
- Sealant Requirement: Generally does not require thread sealant.
Key Differences between NPT and G thread
| Feature | NPT | G Thread |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Profile | Tapered | Parallel |
| Sealing Mechanism | Compression from taper | Gaskets or O-rings |
| Sealant Requirement | Typically required | Generally not required |
Understanding the distinct characteristics of NPT and G threads is crucial for selecting the appropriate fittings and ensuring proper installation and leak-free performance in various applications.
Are NPT and G Threads Compatible?
No, NPT and G threads are not compatible.
- NPT (National Pipe Taper) threads have a 60-degree angle and a tapered profile. They rely on this taper to create a seal as the male threads are screwed into the female counterpart.
- G threads (also known as BSPP or British Standard Pipe Parallel) have a 55-degree angle and a parallel profile. They do not rely on taper for sealing and typically use gaskets or O-rings to create a seal.
Attempting to connect NPT and G threads will result in an improper fit, potential leaks, and may even damage the threads.
Always ensure that the threads you are using are compatible to avoid issues and ensure proper system function.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the key differences between NPT and G threads is crucial for ensuring proper connections and leak-free performance in various applications. NPT threads, with their tapered design, rely on compression to create a seal, often requiring the use of thread sealants. G threads, on the other hand, utilize a parallel thread design and typically rely on gaskets or other sealing methods.
For all your hydraulic fitting needs, including NPT, G, and other thread types, contact DF Hydraulics. We offer a wide selection of high-quality fittings at competitive wholesale prices.
Contact us today to request a quote wholesale hydraulic fittings from DF Hydraulics, and experience the difference.






