Accurately measuring pipe threads is a fundamental skill for anyone working with fluid or gas transfer systems. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a DIY enthusiast, understanding how to measure pipe threads ensures proper connections and prevents costly leaks. This guide will walk you through the essential steps and tools needed to measure pipe threads with precision.
Incorrect measurements can lead to mismatched fittings and system failures. By mastering the techniques outlined in this blog, you’ll be able to confidently identify thread types, determine thread sizes, and ensure compatibility between components. This knowledge is crucial for maintaining the integrity and safety of your piping systems.
What Are National Pipe Threads
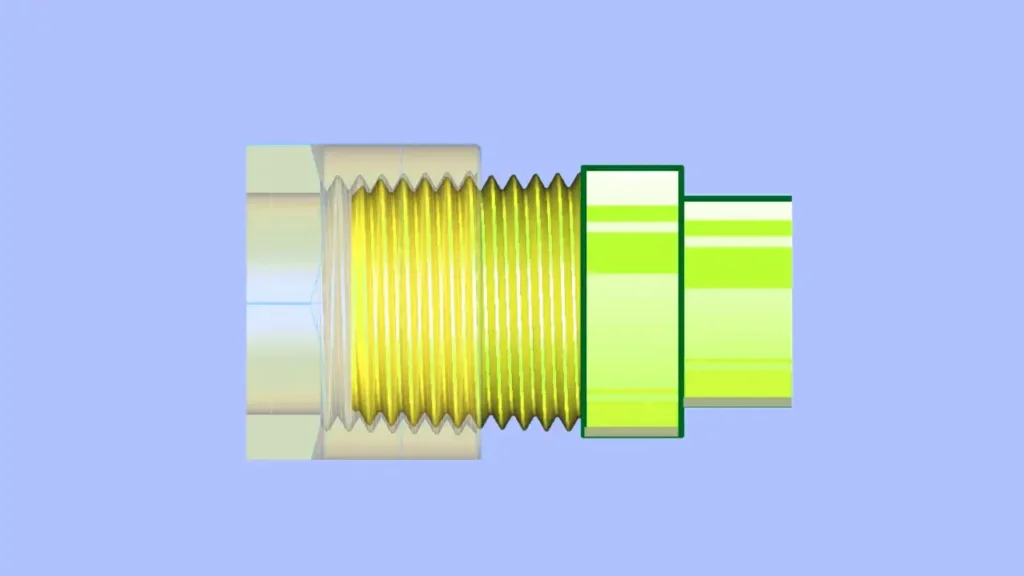
National Pipe Threads (NPT) are a U.S. standard for tapered threads used on threaded pipes and fittings. These threads are designed to create a pressure-tight seal for transporting fluids and gases. The tapered shape of NPT threads, which narrow in diameter along their length, allows them to wedge tightly against each other when screwed together. This creates a mechanical seal, often enhanced with thread sealant, that prevents leaks without the need for additional sealing components like gaskets or O-rings.
NPT threads are widely employed across various industries, including plumbing, oil and gas, and manufacturing, due to their reliability and versatility. Standardized by ANSI/ASME B1.20.1, NPT threads are available in a range of sizes to accommodate different pipe and fitting dimensions. Understanding NPT is crucial for ensuring proper connections and preventing leaks in piping systems, as incorrect thread matching can lead to system failures and safety hazards.
How to Measure Pipe Thread?

Accurately measuring pipe threads is crucial for ensuring proper connections and preventing leaks in fluid and gas transfer systems. Incorrect measurements can lead to mismatched fittings, resulting in system failures. Here’s a detailed guide on how to measure pipe threads.
Tools Needed
- Caliper or thread gauge
- Thread pitch gauge or thread counter
- Taper gauge (for tapered threads)
- Ruler or measuring tape
- Lighting
Step 1: Identifying the Thread Type
Before you begin measuring, you must identify the type of pipe thread you’re working with. Common thread types include NPT (National Pipe Thread), NPTF (National Pipe Thread Fuel), BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper), and BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel). The thread type dictates the measurement methods and tools you’ll need. Visual inspection can sometimes provide clues; tapered threads typically indicate NPT or BSPT, while straight threads suggest NPS or BSPP.
Understanding the thread type is the foundational step. Each type has distinct characteristics that affect measurement and compatibility. Correct identification ensures you use the appropriate tools and methods, leading to accurate results. This preliminary step prevents errors and saves time in the long run.
Step 2: Measuring the Thread Diameter
Using a caliper or thread gauge, measure the outside diameter (OD) of a male thread or the inside diameter (ID) of a female thread. For tapered threads like NPT or BSPT, measure the diameter at the first full thread from the end to capture the most accurate reading.
For straight threads, such as NPS or BSPP, measure the diameter at any point along the thread length. Record the measurement in inches or millimeters, depending on the thread standard you are working with.
Accurate diameter measurements are essential for selecting compatible fittings. This step requires precision, as even slight discrepancies can lead to leaks or improper connections. Consistent and careful measurements are vital for ensuring a reliable fit. The measurements will be used to help identify the nominal pipe size.
Step 3: Measuring Threads Per Inch (TPI) or Pitch
To determine the threads per inch (TPI) for inch-based threads or the pitch for metric threads, use a thread pitch gauge or thread counter. A thread pitch gauge contains a series of blades with different thread pitches; match the blades to the threads until one fits snugly. For metric threads, the pitch is the distance between two adjacent threads, typically measured in millimeters. Record the TPI or pitch measurement accurately.
This step is critical for identifying the thread size and ensuring compatibility with mating fittings. Accurate TPI or pitch measurements are essential for creating a leak-free connection. A thread pitch gauge provides a quick and accurate means of measuring the threads.
Step 4: Determining Thread Taper (for Tapered Threads)
If you’re working with tapered threads like NPT or BSPT, determining the thread taper is essential. The standard taper for NPT is 1/16 inch per inch, while BSPT has a different taper. You can use a taper gauge or measure the diameter at two points along the thread and calculate the difference to determine the taper. While less common, this step is crucial for ensuring compatibility with tapered fittings and preventing leaks.
Measuring the thread taper ensures a proper seal with tapered fittings. This step is crucial for preventing leaks and ensuring a secure connection. The taper measurement helps to confirm the correct fitting size and type.
How to Measure Male Pipe Thread

Accurately measuring male pipe threads is crucial for selecting compatible fittings and preventing leaks in fluid and gas transfer systems. Incorrect measurements can lead to mismatched fittings, resulting in system failures.
Here’s a detailed guide on how to measure male pipe threads.
Tools Needed
- Caliper or thread gauge
- Thread pitch gauge or thread counter
- Ruler or measuring tape
- Lighting
Step 1: Identifying the Thread Type
Before you begin measuring, it’s essential to identify the type of male pipe thread you’re working with. Common thread types include NPT (National Pipe Thread), NPTF (National Pipe Thread Fuel), and BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper). The thread type determines the measurement methods and tools you’ll need. Visual inspection can sometimes help; tapered threads indicate NPT or BSPT, while straight threads suggest NPS or BSPP.
Understanding the thread type is the foundational step. Each type has distinct characteristics that affect measurement and compatibility. Correct identification ensures you use the appropriate tools and methods, leading to accurate results. This preliminary step prevents errors and saves time in the long run.
Step 2: Measuring the Outside Diameter (OD)
Using a caliper or thread gauge, measure the outside diameter (OD) of the male thread at the first full thread from the end. This measurement is crucial for determining the nominal pipe size and selecting compatible female fittings. Ensure the caliper is positioned perpendicular to the thread axis for accurate readings. Record the measurement in inches or millimeters, depending on the thread standard you are working with.
Accurate diameter measurements are essential for selecting compatible fittings. This step requires precision, as even slight discrepancies can lead to leaks or improper connections. Consistent and careful measurements are vital for ensuring a reliable fit. The measurements will be used to help identify the nominal pipe size.
Step 3: Measuring Threads Per Inch (TPI) or Pitch
To determine the threads per inch (TPI) for inch-based threads or the pitch for metric threads, use a thread pitch gauge or thread counter. A thread pitch gauge contains a series of blades with different thread pitches; match the blades to the threads until one fits snugly. For metric threads, the pitch is the distance between two adjacent threads, typically measured in millimeters. Record the TPI or pitch measurement accurately.
This step is critical for identifying the thread size and ensuring compatibility with mating fittings. Accurate TPI or pitch measurements are essential for creating a leak-free connection. A thread pitch gauge provides a quick and accurate means of measuring the threads.
Step 4: Determining Thread Taper (for Tapered Threads)
If you’re working with tapered threads like NPT or BSPT, determining the thread taper is essential. The standard taper for NPT is 1/16 inch per inch, while BSPT has a different taper. You can measure the diameter at two points along the thread and calculate the difference to determine the taper. While less common, this step is crucial for ensuring compatibility with tapered fittings and preventing leaks.
Measuring the thread taper ensures a proper seal with tapered fittings. This step is crucial for preventing leaks and ensuring a secure connection. The taper measurement helps to confirm the correct fitting size and type.
How to Measure Female Pipe Thread
Accurately measuring female pipe threads is crucial for selecting compatible fittings and preventing leaks in fluid and gas transfer systems. Incorrect measurements can lead to mismatched fittings, resulting in system failures.
Here’s a detailed guide on how to measure female pipe threads.
Tools Needed
- Caliper or thread gauge
- Thread pitch gauge or thread counter
- Ruler or measuring tape
- Lighting
Step 1: Identifying the Thread Type
Before you begin measuring, it’s essential to identify the type of female pipe thread you’re working with. Common thread types include FNPT (Female National Pipe Thread), NPTF (National Pipe Thread Fuel), and BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel). The thread type determines the measurement methods and tools you’ll need. Visual inspection can sometimes help; tapered threads indicate FNPT or BSPT, while straight threads suggest NPS or BSPP.
Understanding the thread type is the foundational step. Each type has distinct characteristics that affect measurement and compatibility. Correct identification ensures you use the appropriate tools and methods, leading to accurate results. This preliminary step prevents errors and saves time in the long run.
Step 2: Measuring the Inside Diameter (ID)
Using a caliper or thread gauge, measure the inside diameter (ID) of the female thread at the first full thread from the opening. This measurement is crucial for determining the nominal pipe size and selecting compatible male fittings. Ensure the caliper is positioned perpendicular to the thread axis for accurate readings. Record the measurement in inches or millimeters, depending on the thread standard you are working with.
Accurate diameter measurements are essential for selecting compatible fittings. This step requires precision, as even slight discrepancies can lead to leaks or improper connections. Consistent and careful measurements are vital for ensuring a reliable fit. The measurements will be used to help identify the nominal pipe size.
Step 3: Measuring Threads Per Inch (TPI) or Pitch
To determine the threads per inch (TPI) for inch-based threads or the pitch for metric threads, use a thread pitch gauge or thread counter. A thread pitch gauge contains a series of blades with different thread pitches; match the blades to the threads until one fits snugly. For metric threads, the pitch is the distance between two adjacent threads, typically measured in millimeters. Record the TPI or pitch measurement accurately.
This step is critical for identifying the thread size and ensuring compatibility with mating fittings. Accurate TPI or pitch measurements are essential for creating a leak-free connection. A thread pitch gauge provides a quick and accurate means of measuring the threads.
Step 4: Determining Thread Taper (for Tapered Threads)
If you’re working with tapered threads like FNPT or BSPT, determining the thread taper is essential. The standard taper for FNPT is 1/16 inch per inch, while BSPT has a different taper. You can measure the diameter at two points along the thread and calculate the difference to determine the taper. While less common, this step is crucial for ensuring compatibility with tapered fittings and preventing leaks.
Measuring the thread taper ensures a proper seal with tapered fittings. This step is crucial for preventing leaks and ensuring a secure connection. The taper measurement helps to confirm the correct fitting size and type.
Pipe Thread Measurement Chart
A pipe thread measurement chart is an essential tool for anyone working with pipes and fittings. It provides standardized dimensions for various pipe thread types, including NPT (National Pipe Thread), NPTF (National Pipe Thread Fuel), BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper), and BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel). These charts help users determine the nominal pipe size, thread diameter, and threads per inch (TPI) or pitch, ensuring proper connections and preventing leaks.
Using a pipe thread measurement chart is crucial for selecting compatible fittings and avoiding costly mistakes. The chart’s data allows for accurate identification of thread sizes and types, which is vital for maintaining system integrity in fluid and gas transfer applications. By referring to these charts, users can confidently choose the correct fittings, ensuring reliable and leak-free connections.
| Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) | Outer Diameter (OD) (inches) | Threads Per Inch (TPI) (NPT) | Pitch (mm) (BSP) |
| 1/8″ | 0.405 | 27 | 28 |
| 1/4″ | 0.540 | 18 | 19 |
| 3/8″ | 0.675 | 18 | 19 |
| 1/2″ | 0.840 | 14 | 14 |
| 3/4″ | 1.050 | 14 | 14 |
| 1″ | 1.315 | 11.5 | 11 |
| 1 1/4″ | 1.660 | 11.5 | 11 |
| 1 1/2″ | 1.900 | 11.5 | 11 |
| 2″ | 2.375 | 11.5 | 11 |
| 2 1/2″ | 2.875 | 8 | 11 |
| 3″ | 3.500 | 8 | 11 |
| 4″ | 4.500 | 8 | 11 |
| 5″ | 5.563 | 8 | 11 |
| 6″ | 6.625 | 8 | 11 |
Conclusion
In conclusion, accurately measuring pipe threads is essential for ensuring proper connections and preventing costly leaks in fluid and gas transfer systems. Understanding the different thread types, such as NPT, NPTF, and BSPT, and using the correct measurement tools are crucial for obtaining precise dimensions. This knowledge enables you to select compatible fittings and maintain system integrity.
Following the outlined steps for measuring thread diameter, threads per inch or pitch, and thread taper ensures accurate results. Regular practice and attention to detail minimize errors, leading to reliable and leak-free connections. Proper measurement techniques save time and resources by preventing mismatched fittings and system failures.
For a comprehensive selection of high-quality national pipe threads and expert guidance, choose DF Hydraulics. We offer wholesale options with diverse sizes and materials to meet your specific needs. Contact us today to explore our product offerings and ensure your systems operate with optimal safety and efficiency.



