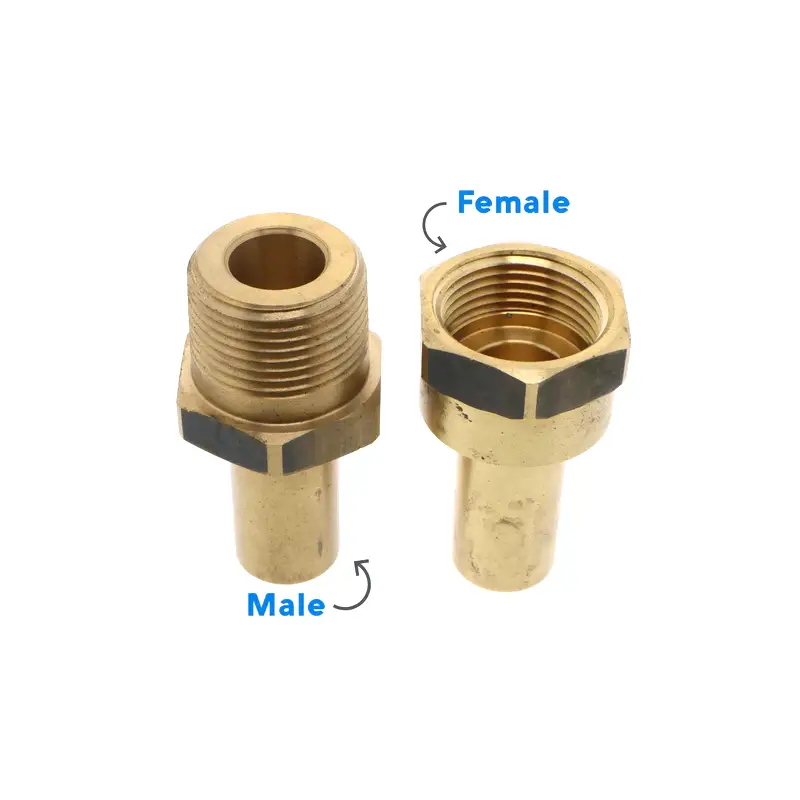
Understanding the distinction between male and female fittings is crucial for anyone working with plumbing, hydraulics, or any fluid transfer systems. This blog post will demystify these fittings, explaining their fundamental differences and how they function within various applications. We’ll explore the visual cues and functional roles that separate male from female fittings, providing a clear guide for accurate identification.
Accurate identification of male and female fittings prevents costly mistakes and ensures secure, leak-free connections. We’ll delve into the practical aspects of these fittings, covering their common uses and the importance of selecting the correct type for specific applications. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a seasoned professional, this guide will provide valuable insights into the world of fittings.
What Are Male Fittings
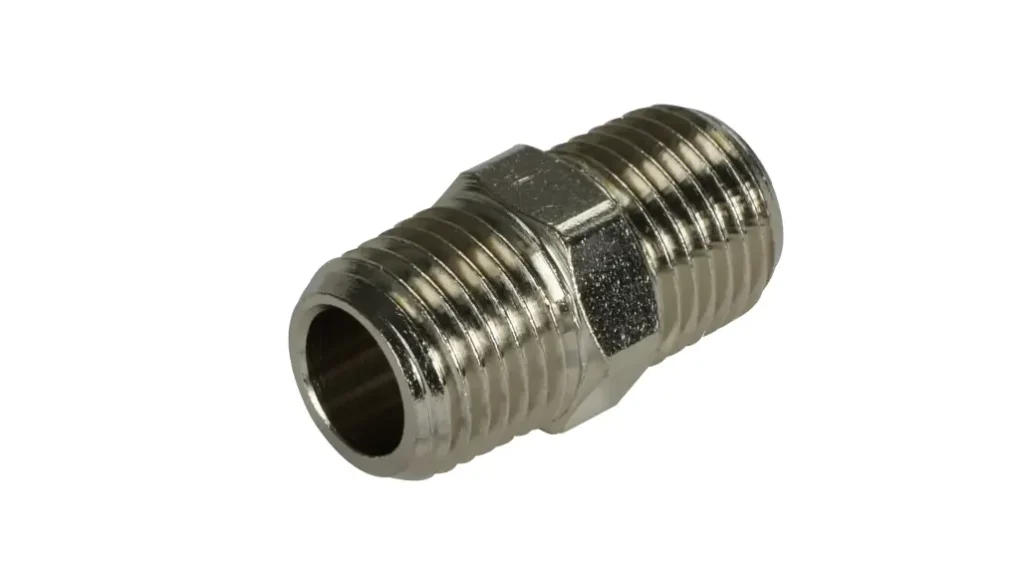

Male fittings are connection components characterized by external threads. These threads are designed to engage with the internal threads of a corresponding female fitting, creating a secure and often leak-proof connection. The external threading is the defining feature, allowing the male fitting to be inserted into a female counterpart, much like a bolt into a nut. They are fundamental in various fluid transfer and piping systems, facilitating the joining of pipes, hoses, valves, and other components.
The applications for male fittings are vast, spanning across industries like plumbing, hydraulics, pneumatics, and automotive. They are manufactured from a range of materials, including brass, stainless steel, and various plastics, to suit different environmental and operational requirements. The specific thread type, such as NPT, BSP, or JIC, is also crucial for compatibility with other components in the system. Male fittings are essential for creating customized piping and fluid transfer solutions, allowing for flexibility and adaptability in complex installations. To summarize:
- Key Feature: External threading.
- Function: To engage with internal threads of female fittings.
- Applications: Wide range, including plumbing, hydraulic, and pneumatic systems.
- Materials: Brass, stainless steel, plastics, and others.
- Thread Types: NPT, BSP, JIC, and others, dictating compatibility.
What Are Female Fittings
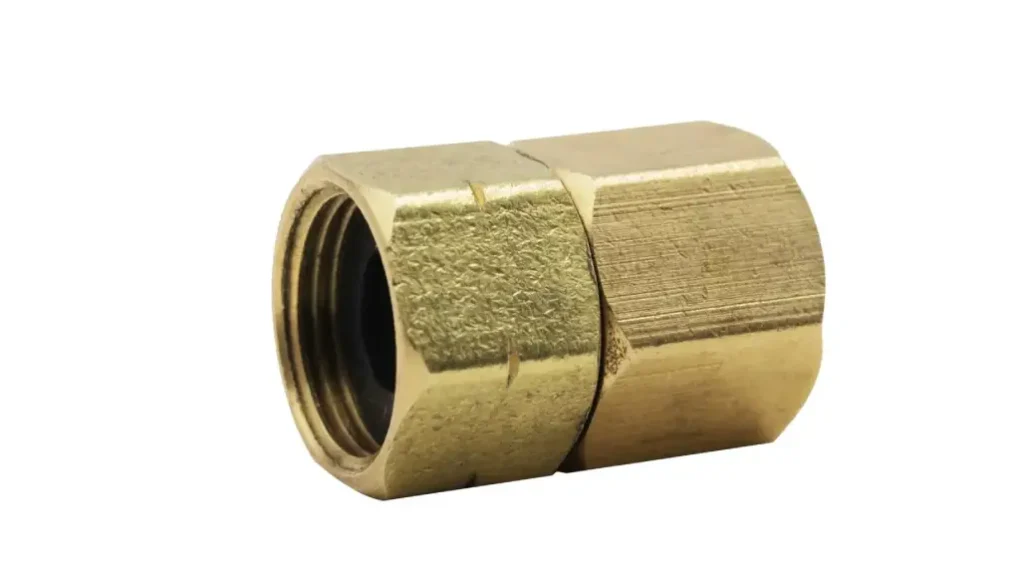

Female fittings are characterized by internal threads. These internal threads are designed to receive and engage with the external threads of a corresponding male fitting, creating a secure connection. This interaction is analogous to a nut receiving a bolt, where the nut (female) has internal threads to accommodate the bolt (male). They are essential components in fluid transfer and piping systems, enabling the connection of various pipes, hoses, valves, and other components.
Female fittings are manufactured from a wide range of materials, including metals like brass and stainless steel, as well as various plastics, to suit diverse application requirements. The selection of materials and thread types (such as NPT, BSP, or JIC) ensures compatibility with other components in the system. They are widely used in plumbing, hydraulic, pneumatic, and automotive applications, providing a reliable means of connecting and sealing fluid or gas lines. To summarize:
- Key Feature: Internal threading.
- Function: To receive and engage with external threads of male fittings.
- Applications: Wide range, including plumbing, hydraulic, and pneumatic systems.
- Materials: Brass, stainless steel, plastics, and others.
- Thread Types: NPT, BSP, JIC, and others, dictating compatibility.
Male vs Female Fittings
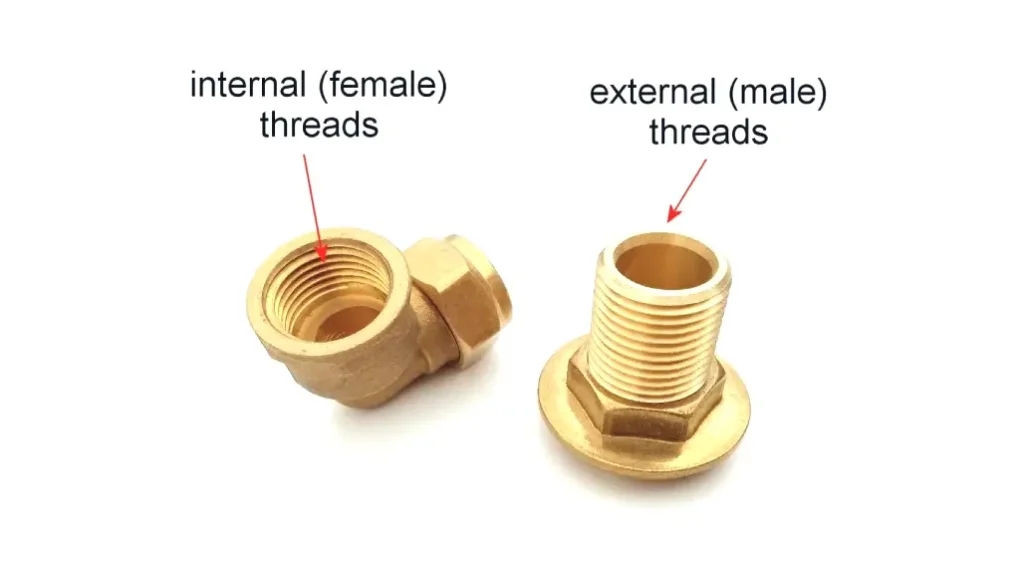
Male and female fittings are fundamental components in various fluid transfer systems, including plumbing, hydraulics, and pneumatics. Their primary function is to connect pipes, hoses, valves, and other components, enabling the flow of liquids or gases. Understanding the distinction between these fittings is crucial for ensuring proper connections and preventing leaks.
The key difference between male and female fittings lies in the location of their threads. Male fittings feature external threads, meaning the threads are located on the outside of the fitting. Conversely, female fittings have internal threads, with the threads located on the inside. This difference dictates how they connect; male fittings are designed to screw into female fittings.
This distinction is essential for compatibility and proper sealing. When selecting fittings for a project, it’s vital to ensure that male and female fittings are correctly matched to create a secure and leak-free connection. The correct pairing ensures efficient fluid transfer and prevents system failures.
| Fitting Type | Thread Location | Function |
| Male | External Threads | Inserts into female fittings |
| Female | Internal Threads | Receives male fittings |
Male to Female Fittings
Male-to-female fittings are essential components in various fluid transfer systems, designed to bridge the gap between connections with differing thread types. These fittings allow for the seamless integration of male-threaded components, such as pipes or valves, with female-threaded components, like hoses or other fittings. They play a crucial role in adapting and connecting diverse components within plumbing, hydraulic, pneumatic, and other fluid handling applications.
The versatility of male-to-female fittings stems from their availability in various materials, sizes, and thread standards. This adaptability ensures compatibility across a wide range of systems and applications. These fittings are crucial for creating custom connections, adapting existing systems, and ensuring leak-free performance.
- Adaptability: They connect components with different thread types.
- Compatibility: They enable connections between different thread standards (e.g., NPT, BSP, JIC).
- Material Variety: Available in materials like brass, stainless steel, and plastic.
- Application Versatility: Used in plumbing, hydraulics, pneumatics, and more.
- System Integration: Facilitate the integration of diverse components into cohesive systems.
How to Choose Male and Female Fittings
Choosing the right male and female fittings requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure compatibility and optimal performance. First, identify the thread type and size required for your application.
Common thread types include NPT, BSP, and JIC, each with specific dimensions and thread pitches. Ensure that the male and female fittings you select have matching thread types and sizes to create a secure, leak-free connection. Additionally, consider the material of the fittings, selecting materials like brass, stainless steel, or plastic based on the fluid or gas being conveyed and the environmental conditions.
Beyond thread specifics, assess the application’s pressure and temperature requirements. Confirm that the chosen fittings are rated for the maximum pressure and temperature expected in your system. Also, consider the ease of installation and maintenance. For applications requiring frequent disconnection, union fittings or quick-connect fittings may be preferred. Finally, always verify the compatibility of the fitting materials with the fluids or gases they will handle to prevent corrosion or degradation. To summarize the key selection points:
Thread Compatibility:
- Match thread types (NPT, BSP, JIC, etc.).
- Ensure correct thread size and pitch.
Material Selection:
- Choose materials based on fluid/gas type (brass, stainless steel, plastic).
- Consider environmental conditions.
Pressure and Temperature Ratings:
- Verify fittings meet maximum system pressure.
- Confirm fittings are rated for operating temperatures.
Application-Specific Needs:
- Consider ease of installation and maintenance.
- Select union or quick-connect fittings for frequent disconnections.
Chemical Compatibility:
- Verify the fitting material is compatible with the fluids used.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between male and female fittings is crucial for any project involving fluid transfer or piping. The simple difference in threading location—external for male, internal for female—dictates compatibility and ensures proper connections. Recognizing these differences prevents costly errors and ensures efficient system functionality. Whether for simple home repairs or complex industrial installations, accurate identification is key.
This knowledge empowers you to select the right fittings for your needs, avoiding leaks and connection failures. By mastering this fundamental concept, you enhance your ability to create reliable and efficient systems. Proper fitting selection optimizes performance and extends the lifespan of your equipment.
Ready to secure high-quality male and female hydraulic fittings for your wholesale needs? Contact DF Hydraulics today for competitive pricing and a comprehensive selection of durable, reliable fittings. We are your trusted partner for all hydraulic fitting solutions.



