AN (Army-Navy) fittings are high-performance, robust connectors widely used in demanding applications like aerospace, motorsports, and hydraulics. Known for their reliability and ability to withstand extreme pressures and vibrations, AN fittings are a critical component in systems where leaks are unacceptable. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of AN fittings, exploring their design, applications, and best practices for installation.
Understanding AN fittings is essential for anyone working with high-performance fluid systems. This guide will cover everything from the different types of AN fittings and their sizing conventions to the proper techniques for assembly and maintenance. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting to learn about AN fittings, this guide will provide valuable insights into these essential connectors.
What Are AN Fittings

AN fittings, short for Army-Navy fittings, are a type of fluid fitting widely used in high-performance applications where reliability and leak-free connections are critical.
Originally developed for military aircraft during World War II, these fittings have become a standard in various industries, including aerospace, motorsports, and high-performance automotive.
AN fittings utilize a 37-degree flare angle to create a metal-to-metal seal between the fitting and the tubing, ensuring a robust and leak-free connection even under high pressure and vibration. They are made from lightweight yet strong materials like aluminum and are known for their durability and resistance to corrosion. AN fittings are available in a wide range of sizes and configurations to accommodate various fluid types and applications.
AN Fitting Sizes
AN fitting sizes can be confusing at first, but understanding the system is key to selecting the right fitting for your application. The sizing system uses a dash number, like AN-6, where the number represents the nominal size in 1/16th of an inch.
This nominal size often correlates to the inner diameter of the hose the fitting is designed to accommodate. It’s crucial to match the AN fitting size to the correct hose size for a secure and leak-free connection.
While the dash number primarily indicates the size, each AN size also has a corresponding thread size. For example, an AN-6 fitting has a 6/16″ (3/8″) nominal size and a 3/8″-24 thread. An AN-8 fitting, on the other hand, has an 8/16″ (1/2″) nominal size and a 7/16″-20 thread. This difference in thread size is important to ensure compatibility with other components in the system.
Here’s a table summarizing the most common AN fitting sizes, their nominal sizes, and thread sizes:
| AN Size | Nominal Size (inches) | Thread Size (inches) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| AN-4 | 4/16 (1/4) | 1/4″-28 | Small fluid lines, instrumentation |
| AN-6 | 6/16 (3/8) | 3/8″-24 | Fuel lines, oil lines, coolant lines |
| AN-8 | 8/16 (1/2) | 7/16″-20 | Fuel lines, oil lines, hydraulic lines |
| AN-10 | 10/16 (5/8) | 9/16″-18 | High-flow fuel lines, hydraulic lines |
| AN-12 | 12/16 (3/4) | 3/4″-16 | Large fuel lines, high-flow hydraulic lines |
| AN-16 | 16/16 (1) | 1″-12 | Large hydraulic lines, specialized applications |
| AN-20 | 20/16 (1 1/4) | 1 5/16″-12 | Very large hydraulic lines, specialized applications |
What Are AN Fittings Used for
AN fittings are primarily used in high-performance fluid systems where reliability and leak-free connections are critical.
Here are some common AN fitting applications:
- Aerospace: AN fittings are essential in aircraft fuel systems, hydraulic lines, and other fluid transfer applications due to their ability to withstand extreme pressures, temperatures, and vibrations.
- Motorsports: In racing vehicles, AN fittings are widely used in fuel systems, oil lines, coolant lines, and brake systems where high performance and resistance to vibration are crucial.
- Automotive: AN fittings are popular in high-performance and custom automotive builds for fuel systems, oil coolers, brake lines, and power steering systems.
- Industrial: AN fittings can also be found in industrial hydraulic systems, fluid transfer applications, and other demanding environments where reliable connections are necessary.
Essentially, AN fittings are used in any application where a robust, leak-free, and high-performance fluid connection is required.
AN Fitting Types and Applications
AN fittings, with their 37-degree flare and lightweight aluminum construction, are versatile components used across various high-performance applications. They are essential in environments demanding reliable, leak-free connections under high pressure and stress.
Here’s a table showing common AN fitting types and their uses:
| Fitting Type | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Straight | Connects two hoses or tubes in a straight line. | Fuel lines, oil lines, coolant lines |
| Elbow (45°/90°) | Changes the direction of fluid flow. | Routing lines in tight spaces, navigating obstacles |
| Tee | Creates a branching point in a fluid system. | Distributing fluid to multiple components |
| Union | Joins two hoses or tubes, allowing for easy disconnection. | Systems requiring frequent maintenance or component replacement |
| Bulkhead | Passes through a panel or wall, creating a secure connection. | Connecting lines through firewalls or bulkheads |
| Adapter | Connects AN fittings to other types of fittings or ports. | Adapting to different thread types or connection styles |
This chart above highlights some of the common types, but the versatility of AN fittings extends to various specialized configurations designed for specific needs.
Advantages of Using AN Fittings
AN fittings offer a compelling combination of features that make them a top choice for demanding fluid transfer applications. Here’s a breakdown of their key advantages:
- Reliable Seal: The 37-degree flare design creates a robust, leak-free seal that can withstand high pressures and vibrations. This is crucial in applications where fluid loss or leakage could have serious consequences.
- High-Pressure Capability: AN fittings are engineered to handle high pressures, making them suitable for demanding hydraulic and fluid power systems.
- Durable Construction: Typically made from lightweight yet strong aluminum, AN fittings offer excellent durability and corrosion resistance. They can also be found in stainless steel for even more extreme environments.
- Standardized Sizing: The AN sizing system (e.g., AN-4, AN-6) provides a clear and consistent way to specify fittings, ensuring compatibility and simplifying component selection.
- Versatility: With a wide range of configurations (straight, elbow, tee, etc.), AN fittings can be adapted to various plumbing needs and system layouts.
- Ease of Assembly and Disassembly: While requiring proper technique, AN fittings are relatively straightforward to assemble and disassemble, facilitating maintenance and modifications.
- High-Flow Capacity: The design of AN fittings promotes efficient fluid flow, minimizing pressure drop and maximizing performance.
These advantages make AN fittings a preferred choice in aerospace, motorsports, high-performance automotive, and other applications where reliability, performance, and durability are paramount.
How to Install AN Fittings?
Installing AN fittings involves a few key steps to ensure a reliable, leak-free connection. Here is the process about how are AN fittings installed in the following:
Prepare the Hose AN Fittings:
- Cut the Hose: Use a sharp cutting tool (like a hose cutter or a fine-toothed saw) to cut the hose to the desired length. For braided hoses, it’s often helpful to wrap the cut area with tape before cutting to minimize fraying.
- Clean the Hose: Remove any debris or particles from the cut end of the hose.
Assemble the AN Fitting:
- Slide the Socket: If the AN fitting uses a separate socket, slide it onto the hose first.
- Insert the Hose: Push the hose into the fitting’s nipple, ensuring it’s fully seated. Some fittings may require a twisting motion during insertion.
- Lubricate: Apply a light lubricant (like engine oil) to the fitting’s threads and the inside of the hose to facilitate assembly and prevent damage.
Connect and Tighten AN Fittings:
- Engage Threads: Start threading the fitting’s nipple into the socket (if applicable) by hand.
- Tighten with Wrenches: Use appropriate wrenches (ideally AN wrenches to avoid damage) to tighten the fitting. Ensure the hose doesn’t twist or back out during tightening.
- Torque to Spec: Refer to the manufacturer’s torque specifications for the fitting size to avoid over-tightening. Overtightening can damage the fitting or hose.
Inspect and Test AN Fittings:
- Visual Inspection: Check for any gaps or signs of improper seating.
- Leak Test: Before putting the system into service, perform a leak test using a suitable method (e.g., soapy water solution, pressure testing).
Important Notes:
- Cleanliness is Key: Ensure all components are clean before assembly to prevent contamination.
- Use the Right Tools: Using the correct tools, especially AN wrenches, is essential to avoid damaging the fittings.
- Follow Instructions: Always refer to the specific instructions provided by the fitting manufacturer, as procedures may vary slightly.
- Practice Makes Perfect: If you’re new to AN fittings,If you’re new to AN fittings, it’s a good idea to practice on some scrap hose first.
By following these steps carefully, you can create secure and reliable AN fitting connections for your high-performance fluid systems.
What is the Difference Between JIC and AN Fittings
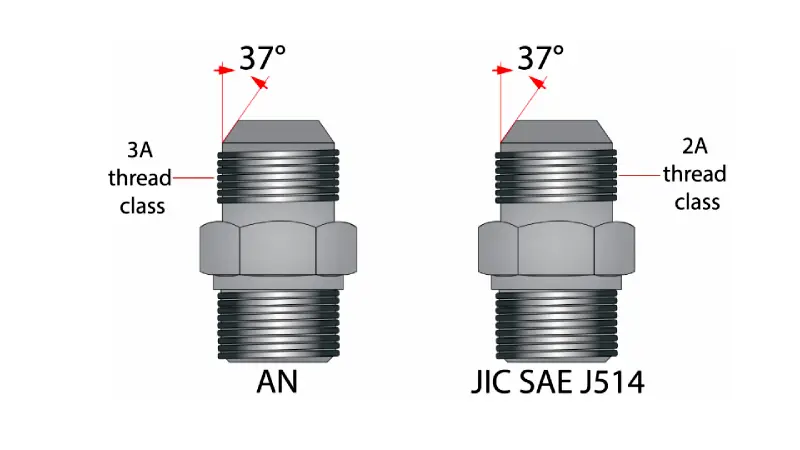
While both JIC (Joint Industry Council) and AN (Army-Navy) fittings utilize a 37-degree flare angle and are used in high-pressure fluid systems, they are not directly interchangeable due to critical differences in manufacturing standards and tolerances. Here’s a breakdown:
- Standard: Developed for general industrial use.
- Tolerances: Manufactured with looser tolerances, making them more cost-effective.
- Applications: Suitable for general hydraulic applications, industrial equipment, and where cost is a primary concern. Less ideal for extreme vibration or high-impulse applications.
- Interchangeability: Not interchangeable with AN fittings due to thread and tolerance differences.
AN Fittings:
- Standard: Designed to stringent military specifications (originally Army-Navy).
- Tolerances: Manufactured to much tighter tolerances, ensuring higher quality and reliability.
- Applications: Preferred for high-performance and critical applications like aerospace, motorsports, and where extreme vibration, pressure, and temperature are factors.
- Interchangeability: Not interchangeable with JIC fittings despite the shared 37-degree flare. While they might physically connect, the differing tolerances could lead to leaks or failures, especially in demanding environments.
Key Differences about JIC fittings and AN fittings
| Feature | JIC Fittings | AN Fittings |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Industrial | Military (Aerospace) |
| Flare Angle | 37 degrees | 37 degrees |
| Tolerances | Looser | Tighter |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | General Hydraulic, Industrial | Aerospace, Motorsports, High-Performance |
| Interchangeable | No | No |
In short: Although both use a 37-degree flare, JIC fittings are for general industrial use, while AN fittings are for high-performance, critical applications. Do not interchange them. Using the wrong fitting can lead to serious consequences.
NPT vs AN Fittings
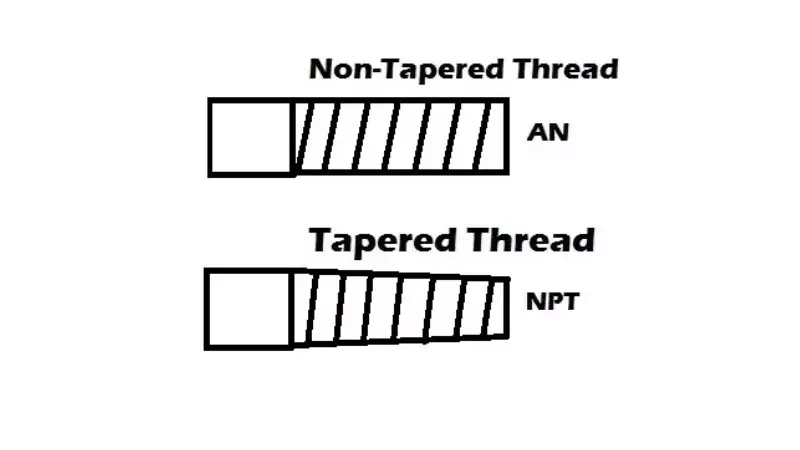
NPT (National Pipe Thread) and AN (Army-Navy) fittings are both used in fluid transfer systems, but they differ significantly in their design, sealing mechanism, and applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right fitting for your needs.
- Type: Tapered pipe thread.
- Seal: Achieved through the interference fit of the tapered threads. Often requires sealant (pipe dope or Teflon tape) to ensure a leak-free seal.
- Applications: Common in plumbing, general industrial applications, and low-pressure systems.
- Pressure Rating: Typically lower than AN fittings.
- Interchangeability: Not interchangeable with AN fittings.
AN Fittings:
- Type: Flare fitting with a 37-degree flare angle.
- Seal: Achieved by the 37-degree flare of the fitting pressing against a matching flare in the mating component. Does not rely on thread sealant.
- Applications: Designed for high-performance and critical applications like aerospace, motorsports, and demanding fluid systems where reliability and leak-free connections are paramount.
- Pressure Rating: Much higher than NPT fittings.
- Interchangeability: Not interchangeable with NPT fittings.
Key Differences Summarized:
| Feature | NPT Fittings | AN Fittings |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Tapered Pipe Thread | Flare Fitting (37-degree) |
| Seal | Thread Interference + Sealant | Flare Contact |
| Pressure Rating | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | Plumbing, General Industrial | Aerospace, Motorsports, High-Performance |
| Interchangeable | No | No |
| Sealant | Required (Pipe Dope, Teflon Tape) | Not Required |
In short: NPT fittings are a general-purpose threaded connection, while AN fittings are specifically designed for high-performance, leak-free, and high-pressure applications. They are fundamentally different and cannot be interchanged. Using the wrong fitting can lead to leaks, system failure, and potentially dangerous situations.
Conclusion
AN fittings stand as a pinnacle of reliable fluid transfer solutions, particularly in demanding applications like aerospace and motorsports. Their robust design, standardized specifications, and ability to withstand extreme conditions make them a preferred choice where performance and safety are paramount. Understanding the nuances of AN fittings, from their sizing and materials to proper installation techniques, is crucial for anyone working with high-performance fluid systems.
This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of AN fittings, covering their various types, applications, and best practices. By grasping these fundamentals, you can confidently select and utilize AN fittings to ensure optimal performance and prevent costly failures in your critical systems.
For high-quality AN fittings at competitive wholesale prices, contact DF Hydraulics today. Our extensive inventory and expert team are ready to assist you in finding the perfect fittings for your specific needs. Get in touch now to discuss your requirements and experience the DF Hydraulics difference.



