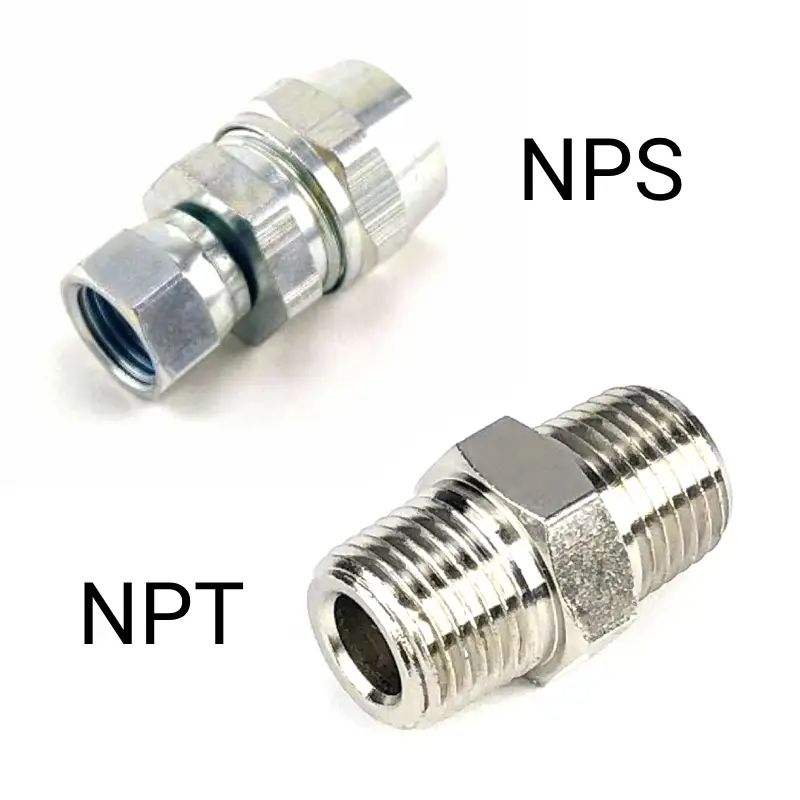
NPS and NPT are two common thread standards used in various industries, but they differ significantly in their design and function. NPS, or Nominal Pipe Size, refers to the nominal inside diameter of a pipe or fitting. It’s important to note that NPS does not directly correspond to the actual inside diameter of the pipe. NPT, on the other hand, stands for National Pipe Taper. It’s a standard for tapered threads commonly found in pipe and fitting connections.
While NPS defines the nominal size, NPT specifies the thread profile. NPT threads are tapered, meaning the diameter of the thread gradually decreases along its length. This tapered design creates a self-sealing mechanism as the male fitting is screwed into the female fitting.
What is NPS
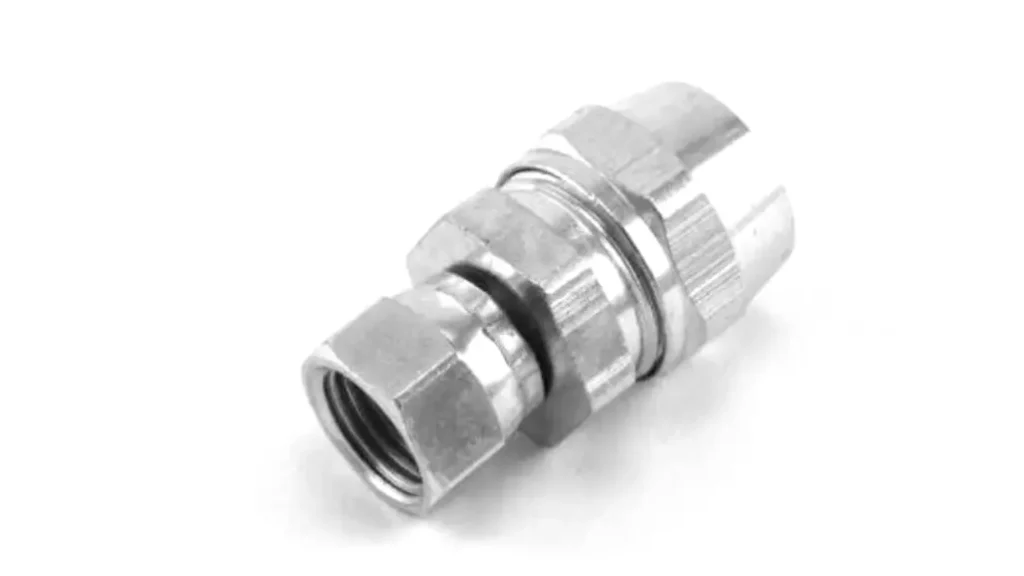

NPS stands for National Pipe Straight. It’s a standard for straight pipe threads, meaning the threads have a constant diameter along their length. Unlike tapered threads (like NPT), NPS threads do not rely on thread deformation to create a seal.
NPS threads are commonly used in applications where:
- External seals are employed: NPS threads often work in conjunction with gaskets or O-rings to create a seal.
- Frequent assembly and disassembly are required: The straight thread design simplifies installation and removal, reducing the risk of galling (thread seizing).
- High-pressure applications are not critical: NPS threads may not be suitable for high-pressure applications due to their reliance on external seals.
What Is NPT
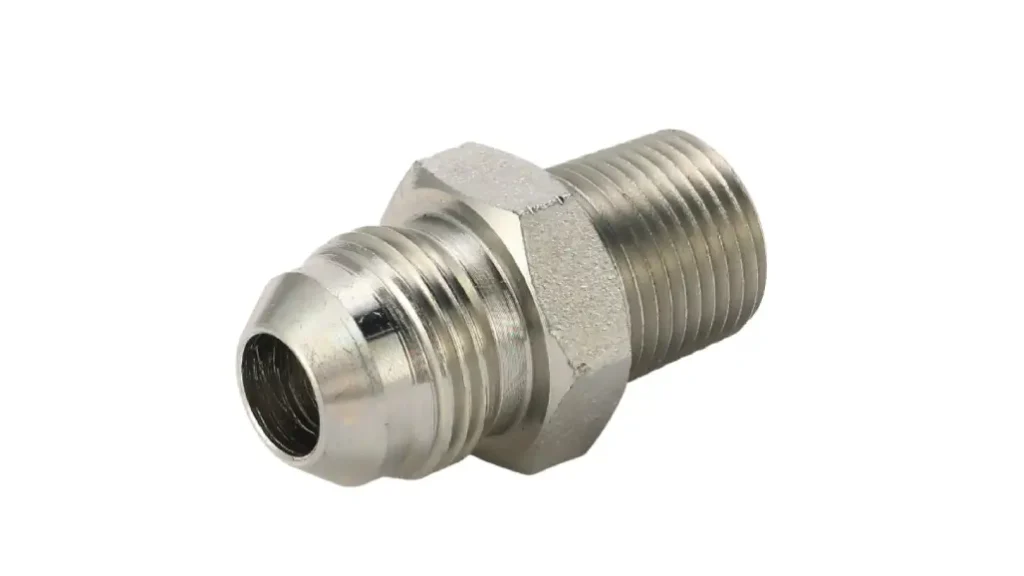

NPT stands for National Pipe Taper.
NPT threads are characterized by a tapered profile. As the male fitting is screwed into the female fitting, the tapered threads compress against each other, creating a tight seal through metal-to-metal contact and deformation. This self-sealing mechanism makes NPT fittings suitable for various applications, from plumbing to hydraulic systems.
NPT threads are widely used in various industries, including plumbing, construction, and industrial machinery.
NPS vs NPT
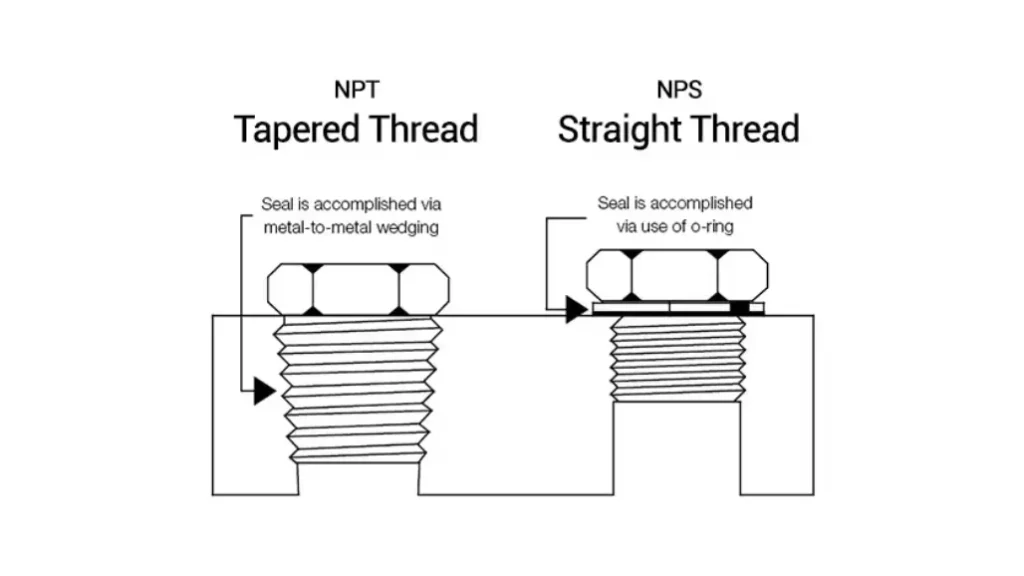
NPS (National Pipe Straight) vs. NPT (National Pipe Taper)
Both NPS and NPT are standards used in piping systems, but they differ significantly in their thread design and sealing mechanisms:
NPS (National Pipe Straight):
Thread Design: Straight threads with a constant diameter along their length.
Sealing Mechanism: Relies on external seals, such as gaskets or O-rings, to create a leak-proof connection. The straight threads themselves do not provide a significant sealing force.
Advantages:
- Easier installation and removal compared to tapered threads.
- Reduced risk of galling (thread seizing) during assembly and disassembly.
- Suitable for applications where external sealing methods are employed.
Disadvantages:
- Limited sealing capability without the use of external seals.
- May not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
NPT (National Pipe Taper):
Thread Design: Tapered threads with a gradually decreasing diameter along their length.
Sealing Mechanism: Creates a self-sealing mechanism. As the male fitting is screwed into the female fitting, the tapered threads compress against each other, forming a tight seal.
Advantages:
- Reliable sealing performance, especially in high-pressure applications.
- Widely used and readily available in various sizes and materials.
Disadvantages:
- Higher risk of galling compared to straight threads.
- Can be more difficult to install and remove.
This table shows you the differences between NPS and NPT fitting threads in the following:
| Feature | NPS (National Pipe Straight) | NPT (National Pipe Taper) |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Design | Straight | Tapered |
| Sealing Mechanism | External seals (gaskets, O-rings) | Self-sealing through thread compression |
| Pressure Capability | Limited | Higher |
| Galling Risk | Lower | Higher |
| Installation/Removal | Easier | More challenging |
| Applications | Applications with external seals, frequent assembly/disassembly | High-pressure applications, general plumbing |
NPS to NPT Adapter
An NPS to NPT adapter is a specialized fitting designed to connect components with different thread types.
- NPS (National Pipe Straight): As discussed earlier, NPS threads are straight and typically require external seals for a leak-proof connection.
- NPT (National Pipe Taper): NPT threads are tapered, creating a self-sealing mechanism through thread deformation.
An NPS to NPT adapter essentially bridges this gap. It has an NPS female end that connects to a component with NPS threads and an NPT male end that connects to a component with NPT threads.
These adapters are crucial when you need to connect components with different thread types within a piping system. They allow for flexibility and compatibility in system design and maintenance.
Are NPT and NPS Threads Compatible
No, NPS (National Pipe Straight) and NPT (National Pipe Taper) threads are not directly compatible for sealing purposes.
- NPS threads are straight, meaning the diameter of the thread remains constant along its length. They rely on external seals, such as gaskets or O-rings, to create a leak-proof connection.
- NPT threads are tapered, creating a self-sealing mechanism through the compression of the threads as they are tightened.
Attempting to directly connect an NPS fitting to an NPT fitting will likely result in:
- Leaks: The straight NPS threads cannot create a reliable seal with the tapered NPT threads, leading to potential leaks.
- Damage: Forcing the connection may damage the threads or the fittings themselves.
To connect components with NPS and NPT threads:
- Use an adapter: An NPS to NPT adapter is specifically designed to bridge this gap. These adapters have an NPS female end and an NPT male end, allowing for a secure connection between components with different thread types.
While NPS and NPT threads may appear similar, their different designs make them incompatible for direct connection. Using appropriate adapters is crucial to ensure a reliable and leak-free connection between components with these thread types.
Conclusion
Understanding the key differences between NPS and NPT threads is crucial for selecting the appropriate fittings for your hydraulic system. NPS (National Pipe Straight) threads are straight and require external seals, while NPT (National Pipe Taper) threads are tapered and create a seal through thread deformation. Choosing the right thread type ensures proper function, prevents leaks, and enhances the overall reliability of your hydraulic system.
Ready to upgrade your hydraulic system with top-quality components? Contact DF Hydraulics today for a free quote on wholesale hydraulic fittings. Our team of experts will work with you to determine the best solution for your specific application and ensure you receive the highest quality components at competitive prices.



