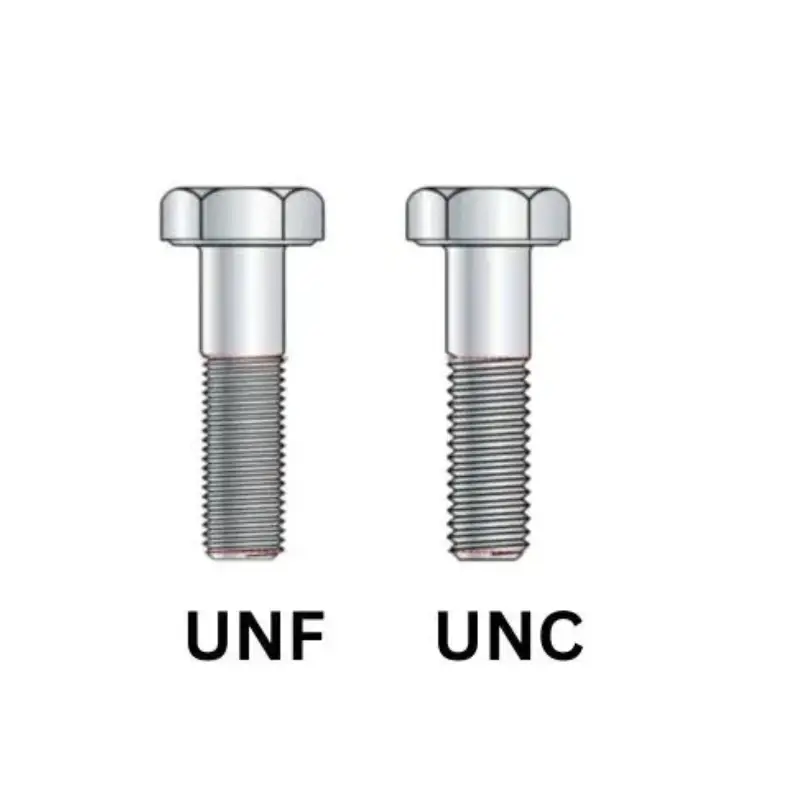
Threads play a crucial role in countless mechanical applications, from fastening components to transmitting power. Two of the most common thread standards are UNC (Unified National Coarse) and UNF (Unified National Fine). While seemingly similar, these standards have distinct characteristics that significantly impact their performance and suitability for different applications.
This article will delve into the key differences between UNC and UNF threads, exploring their size, pitch, strength, and typical applications. By understanding these distinctions, engineers and manufacturers can make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate thread for their projects, optimizing performance and ensuring the reliability of their designs.
What Is UNC

UNC stands for Unified National Coarse. It’s a standard for screw threads commonly used in the United States and other countries.
UNC threads are characterized by a relatively coarse pitch, meaning there are fewer threads per inch compared to finer thread types like UNF (Unified National Fine). This coarser pitch offers several advantages, including easier assembly and disassembly, as well as greater resistance to galling (the seizing of metal threads due to excessive friction).
What Is UNF

UNF stands for Unified National Fine. It’s a standardized thread profile characterized by a fine pitch, meaning it has more threads per inch compared to its coarser counterpart, UNC (Unified National Coarse).
This finer pitch offers several advantages, including:
- Increased Precision: UNF threads provide greater control and finer adjustments in applications requiring precise positioning.
- Enhanced Strength: The higher thread count distributes stress more evenly, leading to improved load-bearing capacity and reduced risk of thread stripping.
- Better Vibration Resistance: The tighter fit provided by the fine pitch offers improved resistance to loosening due to vibration.
These characteristics make UNF threads well-suited for applications where precision, strength, and resistance to vibration are critical.
UNC vs UNF
UNC (Unified National Coarse) vs. UNF (Unified National Fine):
UNC and UNF are two common thread standards within the Unified Thread System. They both define the dimensions and specifications of screw threads, but they differ significantly in their pitch.
UNC (Unified National Coarse):
Characterized by a coarser thread pitch, meaning fewer threads per inch.
Offers several advantages:
- Easier Assembly and Disassembly: The larger thread spacing allows for faster tightening and loosening of fasteners.
- Greater Clearance: The larger spaces between threads provide more clearance for chips or debris to escape, reducing the risk of thread galling (seizing).
- Suitable for applications where frequent assembly and disassembly are required.
UNF (Unified National Fine):
Characterized by a finer thread pitch, meaning more threads per inch.
Offers several advantages:
- Higher Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity: The increased number of threads provides a larger contact area, distributing the load more evenly and improving the overall strength of the joint.
- Improved Vibration Resistance: The tighter fit of the finer threads provides better resistance to loosening caused by vibration.
- Enhanced Precision: UNF threads offer greater precision in applications requiring fine adjustments or positioning.
- Suitable for applications where high strength, vibration resistance, and precise positioning are critical.
| Feature | UNC (Unified National Coarse) | UNF (Unified National Fine) |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Pitch | Coarser (fewer threads per inch) | Finer (more threads per inch) |
| Assembly/Disassembly | Easier | More difficult |
| Strength | Lower | Higher |
| Vibration Resistance | Lower | Higher |
| Precision | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | General applications, frequent assembly/disassembly | High-stress applications, vibration-prone environments, applications requiring precision |
UNF vs UNJF

Both UNF (Unified National Fine) and UNJF (Unified National Joint Fine) are fine-pitch thread standards, but they differ in their design and intended applications.
UNF (Unified National Fine)
Thread Profile: Standard 60-degree flank angle.
Focus: General-purpose fine thread for various applications requiring precision and strength.
Applications:
- Widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
- Suitable for applications requiring:
- High strength and load-bearing capacity.
- Vibration resistance.
- Moderate levels of fatigue resistance.
UNJF (Unified National Joint Fine)
Thread Profile: Modified UNF thread with a larger root radius.
Focus: Enhanced fatigue resistance and durability in high-stress applications.
Applications:
- Specifically designed for applications involving cyclic loading and high stress, such as:
- Aerospace components.
- High-performance automotive parts.
- Military equipment.
- Ideal where fatigue failure is a major concern.
Key Differences
| Feature | UNF | UNJF |
|---|---|---|
| Root Radius | Standard | Larger root radius |
| Fatigue Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Stress Concentration | Moderate | Reduced |
| Applications | General-purpose fine thread | High-stress, cyclic loading applications |
Choosing Between UNF and UNJF
- General Applications: UNF threads are typically sufficient for most applications requiring fine threads.
- High-Stress, Cyclic Loading Applications: UNJF threads offer superior fatigue resistance and are recommended for critical components.
How to choose UNC and UNF Threads
Choosing Between UNC and UNF Threads
Selecting the right thread type (UNC or UNF) depends heavily on the specific requirements of your application. Here’s a breakdown of key factors to consider:
1. Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity:
High-Stress Applications:
- UNF is generally preferred. Its finer pitch provides a larger contact area, distributing the load more evenly and increasing the overall strength of the joint. This is crucial in applications like:
- Aerospace: Where high strength and resistance to vibration are paramount.
- Heavy Machinery: Where components are subjected to significant loads and stresses.
- High-Performance Vehicles: Where lightweight components need to withstand high stresses.
- Lower-Stress Applications:
- UNC may be sufficient. Its coarser threads are easier to engage and offer adequate strength for many general-purpose applications.
2. Ease of Assembly and Disassembly:
Frequent Assembly/Disassembly:
- UNC is generally easier to work with. Its coarser threads allow for faster tightening and loosening, which is important in applications where frequent maintenance or adjustments are required.
Applications Requiring Precision:
UNF offers finer adjustments and more precise positioning due to the smaller distance between threads. This is crucial in:
- Fine Machining: Where precise alignment and positioning are critical.
- Instrumentation: Where accurate adjustments are essential for proper operation.
3. Vibration Resistance:
Vibration-Prone Environments:
- UNF threads provide better resistance to loosening caused by vibration. The tighter fit of the finer threads helps to maintain a secure connection even under dynamic conditions.
4. Application-Specific Considerations:
- Space Constraints: In applications with limited space, UNC threads may be preferable due to their coarser pitch, which can sometimes allow for a slightly shorter overall length.
- Manufacturing Considerations: The availability and cost of tooling and materials can also influence the choice of thread type.
5. Industry Standards and Best Practices:
- Always consult relevant industry standards and best practices for specific applications.
- Consider factors like safety regulations, material compatibility, and corrosion resistance.
By carefully evaluating these factors and considering the specific requirements of your application, you can make an informed decision between UNC and UNF threads to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and safety.
Conclusion
UNC and UNF threads offer distinct advantages and disadvantages depending on the specific application requirements. UNC threads provide greater strength and load-bearing capacity, making them suitable for high-stress applications. UNF threads, on the other hand, offer easier assembly and disassembly, making them ideal for applications where frequent maintenance or adjustments are necessary.
Selecting the appropriate thread type is crucial for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of your components. By carefully considering factors such as the required strength, ease of assembly, and operating conditions, you can make informed decisions to minimize the risk of failure and maximize the efficiency of your systems.
Ready to upgrade your hydraulic systems with top-quality components? Contact DF Hydraulics today for a free quote on wholesale hydraulic fittings. Our team of experts will work with you to determine the best solution for your specific application and ensure you receive the highest quality components at competitive prices.



