Understanding hydraulic fitting orientation is crucial for efficient and leak-free systems. This blog post delves into how to accurately determine hydraulic hose fitting angles, a key aspect of proper installation. We’ll explore the various fitting angles and their applications.
Accurate fitting angle selection prevents hose twisting and premature failure. This guide provides practical tips and visual aids to help you identify and measure fitting angles, ensuring your hydraulic systems operate at peak performance.
What Is Hydraulic Fitting Orientation
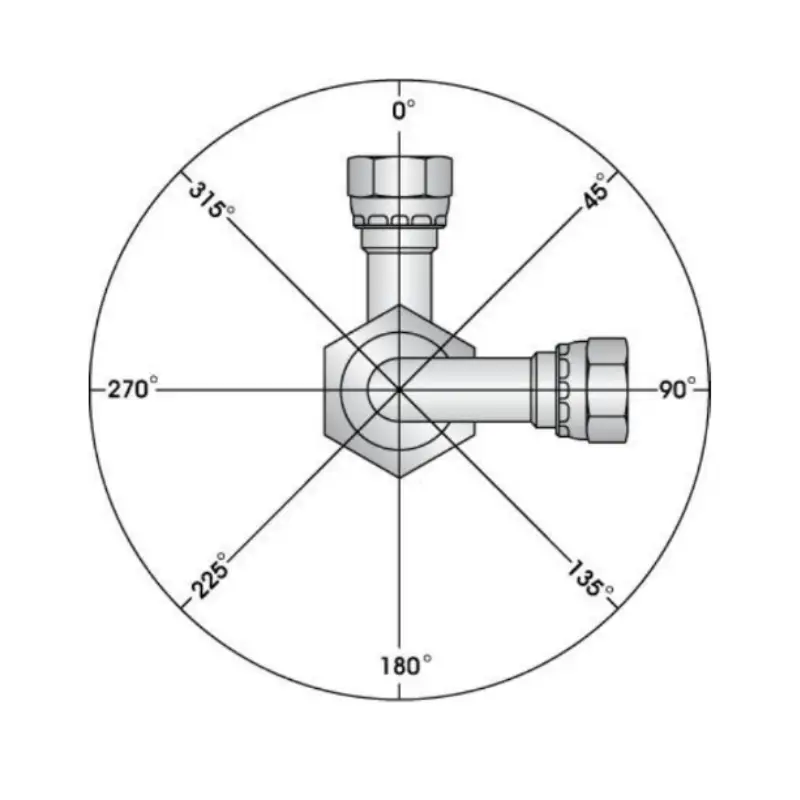
Hydraulic fitting orientation refers to the precise alignment and positioning of hydraulic fittings within a system to ensure optimal fluid flow and prevent leaks. It involves understanding the various angles and configurations of fittings, such as straight, 45-degree, and 90-degree fittings, and how they interact with hoses and other components. Proper orientation considers factors like hose routing, space constraints, and the direction of fluid flow to minimize stress on the fittings and hoses.
Accurate hydraulic fitting orientation is crucial for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of hydraulic systems. Incorrect orientation can lead to premature hose failure, leaks, and reduced system performance. By carefully considering the angles and positions of fittings during installation, engineers and technicians can ensure that the system operates smoothly and reliably. This attention to detail is essential for preventing costly downtime and ensuring the longevity of hydraulic equipment.
How to Measure Hydraulic Fitting Orientation
Accurate hydraulic fitting orientation is vital for system efficiency and leak prevention. Measuring fitting angles ensures proper alignment and fluid flow. This guide provides a step-by-step method to precisely determine hydraulic fitting orientation, minimizing errors and maximizing system performance.
Step 1: Identify the Fitting Type and Angle
First, visually inspect the hydraulic fitting to determine its type (e.g., elbow, tee, straight) and the approximate angle of any bends. Elbow fittings, for instance, are commonly available in 45-degree and 90-degree angles. This initial assessment provides a starting point for accurate measurement.
Understanding the fitting’s intended function within the hydraulic system is also critical. A fitting’s design dictates its orientation and how it connects with other components. For example, a 90-degree elbow directs fluid flow perpendicularly, while a tee fitting allows for fluid distribution in three directions.
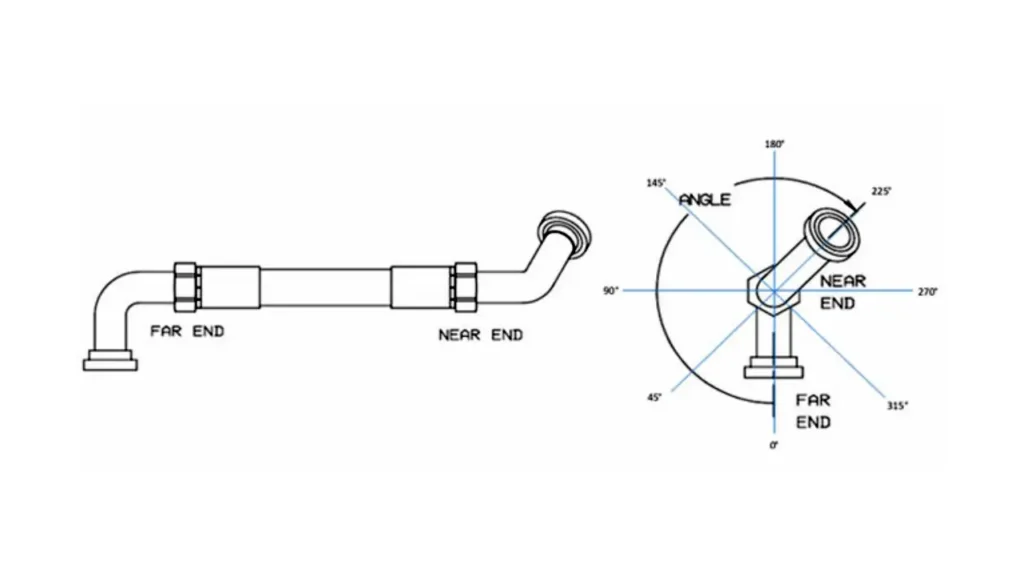
Step 2: Establish a Reference Point
To accurately measure the fitting’s orientation, establish a consistent reference point. This can be a flat surface, a straight edge, or a specific point on the fitting itself. For elbow fittings, it’s often easiest to use the flat surface of one of the fitting’s end connections as a baseline.
Using a stable reference point is essential for consistent and repeatable measurements. This ensures that any subsequent measurements are accurate relative to the initial baseline. A well-defined reference minimizes the risk of errors and provides a reliable foundation for determining the fitting’s orientation.
Step 3: Use a Protractor or Angle Finder
Place a protractor or angle finder against the reference point and the fitting’s angled section. Align the tool’s baseline with the reference point and read the angle measurement where the fitting’s angled section intersects with the tool’s scale. Digital angle finders provide precise readings, while traditional protractors offer a visual representation of the angle.
When using these tools, ensure they are calibrated correctly to avoid measurement errors. Digital angle finders often offer greater precision, especially in tight spaces or complex configurations. Maintaining a steady hand and ensuring the tool is firmly placed against the reference points is vital for accuracy.
Step 4: Verify the Measurement
Repeat the measurement from different angles or using a different tool to verify the accuracy of your initial reading. Cross-referencing measurements helps identify any potential errors or inconsistencies. If possible, compare the measured angle to the fitting’s specifications or manufacturer‘s documentation.
Multiple measurements and comparisons provide a level of confidence in the accuracy of the reading. Verifying the measurement from different perspectives helps to minimize parallax errors and ensure that the angle is consistently measured. This verification process is vital for ensuring the proper functioning of hydraulic systems.
Different Hydraulic Fitting Angles
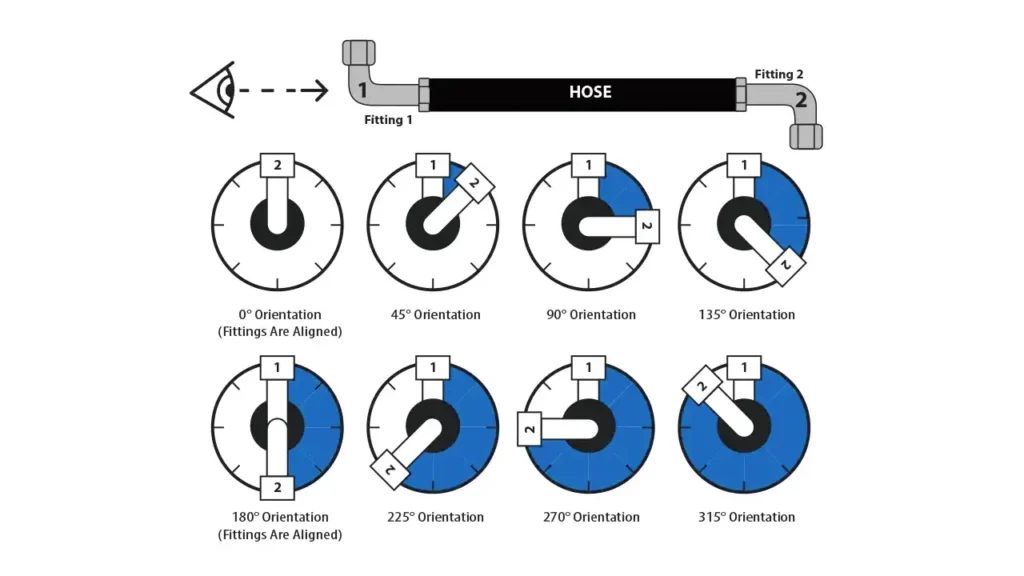
Straight Fittings (0 Degrees)
Straight fittings provide a direct, uninterrupted connection. They are used when hydraulic lines run in a straight path, minimizing pressure drop and ensuring efficient fluid flow. Essential for linear hose or tube connections, their design simplifies installation and maintenance. They are vital for consistent pressure and flow in long runs, found in all hydraulic systems.
45 Degree Fittings
45-degree fittings offer a moderate directional change, providing smooth transitions. They are used for gentle bends around obstacles, minimizing turbulence and pressure drop. Versatile and common, they reduce hose stress, ideal when 90-degree bends are too sharp. They are perfect for tight spaces requiring gradual directional changes.
90 Degree Fittings
90-degree fittings create sharp, perpendicular directional changes. They are used when space is limited, navigating tight corners and complex layouts. Essential for compact systems, their design efficiently routes lines in confined areas. They are crucial for applications requiring rapid directional changes, found in heavy equipment and tools.
180 Degree Fittings (Return Bends)
180-degree fittings facilitate complete fluid flow reversals. They are used when lines double back, creating U-turns in compact systems. Common in heat exchangers, they enable efficient recirculation, vital in space-limited systems. They are essential for compact layouts, allowing fluid returns without complex routing.
225 Degree Fittings
225-degree fittings are essentially a 45-degree fitting in the opposite direction from a 45 degree fitting. They are used when a system needs to both turn and run in a similar direction to the original line, but offset. They are less common than other fittings, but still useful in tight spaces.
They allow for complex routing in systems where space is a premium. They are often used in custom hydraulic systems.
270 Degree Fittings
270-degree fittings are the opposite of a 90 degree fitting. They are used when a system needs to turn and then run parallel to the original line, but offset. They are less common than 90 degree fittings, but are still useful in tight spaces.
They allow for complex routing in systems where space is a premium. They are often used in custom hydraulic systems.
315 Degree Fittings
315-degree fittings are the opposite of a 135 degree fitting. They are used when a wide, sweeping turn in the opposite direction of a 135-degree turn is required to navigate around large obstacles or to achieve specific flow patterns. This angle minimizes pressure drop compared to sharper turns while providing a substantial change in direction.
These fittings are useful in applications where a gradual but significant change in direction is needed. They are often employed in complex hydraulic systems to avoid sharp bends that could cause excessive turbulence. Their design allows for a smoother transition, reducing stress on hoses and fittings.
Adjustable Fittings (Variable Angles)
Adjustable fittings offer flexible, variable-angle solutions. They are used when specific angles are needed, simplifying installation and maintenance in complex layouts. Useful for on-site adjustments, they reduce the need for multiple fixed fittings. They provide adaptability, fine-tuning system layouts, and are beneficial in applications where flexibility is paramount.
Conclusion
Understanding hydraulic fitting orientation is crucial for efficient and leak-free hydraulic system performance. Correctly determining the hydraulic hose fitting angle ensures proper fluid flow and prevents premature hose failure. By following the guidelines outlined, you can accurately select and install fittings, optimizing your system’s reliability and longevity. This knowledge empowers you to maintain and troubleshoot hydraulic systems effectively, reducing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency.
Accurate fitting selection and installation are paramount for preventing costly leaks and system failures. Proper orientation minimizes stress on hoses and fittings, extending their lifespan. Whether you’re working on heavy machinery, automotive systems, or industrial applications, mastering hydraulic fitting angles is essential for achieving optimal performance. This attention to detail ensures your hydraulic systems operate smoothly and efficiently.
For high-quality wholesale hydraulic fittings, including a wide range of angles and sizes, contact DF Hydraulics. We provide durable and reliable solutions tailored to your specific needs. Contact DF Hydraulics today to get a quote on your wholesale hydraulic fitting needs.